Suspension polystyrene foam is one of the most popular insulation materials on the market. The material has really good performance characteristics. And I want to talk about its technical characteristics, scope and other features.
The foam board must be marked.
The main purpose of PSB S 35 is foundation insulation
PSB-S 35 insulation, the technical characteristics of which are very impressive, and the price is within average values, is today one of the most popular on the market. It is used as a heat and sound insulator in the construction of flat exploitable roofs, floors with high load capacity, foundations and basements. More detailed information about the characteristics of the material can be found in the section PSB-S 35 technical characteristics.
Areas of application of PSBS 35
Expanded polystyrene PSB-S 35 is most relevant in structures with high load resistance. Nowadays, when constructing monolithic foundations, polystyrene foam PSB-S 35 is increasingly used as permanent formwork, the characteristics of which allow it to be used very widely, for example, for thermal insulation:
- foundation strips and pile foundations;
- plinths;
- external networks and pipelines;
- flat roofs and attic spaces;
- inversion roofs;
- curtain facades;
- outside brick walls when laying wells;
- attics;
- floors, including warm ones;
- heated sidewalks and platforms, parking lots;
- soil from freezing.
Polystyrene foam PSB-S 35 is also used as:
- diversion;
- permanent formwork forms;
- bases for plaster;
- middle layer in steel and reinforced concrete panels;
- protection for drainage and strengthening of slopes.
Expanded polystyrene 35: advantages
- almost completely impenetrable to wind;
- increased rigidity foam 35 density;
- the price with similar indicators to the M50 is significantly lower;
- minimal thermal conductivity;
- works under high compressive loads;
- PSB S 35 does not provoke active combustion;
- excellent water and biological resistance, does not mold;
- ecologically pure;
- PSBS 35 does not “age” and maintains performance for up to 50 years;
- sales and shipment are carried out for all cities of the Russian Federation.
Why do buyers choose this brand of foam?
Packaging of self-extinguishing polystyrene foam PSB-35.
I will not list the advantages of polystyrene foam as insulation. Those interested can familiarize themselves with them in my other articles on the site. I would like to highlight the differences specifically in the 35th PSB-S.
Another example of PSB-S products.
In short, we can say that this is in a sense a universal material that will suit:
- for wall insulation;
- will not be “afraid” of the foundation or septic tank;
- and can also be used to insulate floors inside an apartment or house.
This is a kind of substitute for an extrusion machine, but cheaper.
Do-it-yourself thermal insulation of the base.
The strength of these sheets is sufficient for use in the construction of heated roads and parking lots, runways, protection of soils from swelling, strengthening of slopes, etc. The instructions allow you to use PSB-S of the thirty-fifth series for these purposes, although personally I would play it safe and buy a PSB-S-50.
In regions with harsh climates, the material can be used on walls.
Features of the material
Polystyrene foam is white sheets with low weight. If we talk about pressless PSB-S, it looks like small balls connected to each other. It contains up to 98% air. Despite this, the technical characteristics of the PSB-S 35 remain at their best.
The abbreviation is deciphered as follows. The letters "PS" stand for "polystyrene". The letter “B” is “pressless”, “C” is “self-extinguishing”. The numbers indicate maximum density. In this case, the specific gravity of the material is in the range of 25-35 kg/m3.
PSB-S 35 is capable of withstanding high loads. In this case, the slab does not sag or move. Polystyrene foam does not absorb water. Due to this, it does not change its size and shape. The mechanical, thermal insulation and technical characteristics of PSB-S 35 do not change throughout the entire service life.
How to determine density yourself
It is important to be able to protect yourself from unscrupulous manufacturers.
As we can see from the list of physical characteristics, such an important indicator as density varies in a fairly large range, from 25 to 35 kg/m³.
If 25-gauge foam is perfect for insulating walls, then for floor insulation you need at least 35-gauge. In this regard, as well as the dishonesty of many manufacturers, it is advisable to be able to find out the real density of the foam.
Visual inspection before purchase is required.
This is not difficult to do. It is necessary to weigh a sheet of polystyrene foam, preferably on an electronic scale, since it is light and large errors will negate all our efforts. Let us denote the weight of the sheet with the letter “m”. Let's say our sheet weighs 1200 grams, convert it to kilograms and get m = 1.2 kg.
Advantages and disadvantages
Among the positive qualities of the material are:
- Vapor tightness.
- Does not absorb water.
- Environmentally friendly.
- Prevents the development of mold and fungi.
- Doesn't rot.
- Does not react with acids, weak alkalis, alcohol and salts.
- Does not react with components of concrete mixtures and other similar building materials.
- Resistant to fire, as it is treated with a fire retardant.
- It is light in weight.
- It is convenient to work during installation (it is easy to cut without emission of dust).
- Long service life (over 35 years).
The PSB-S 35 stove also has its disadvantages. There are few of them compared to the advantages. The main disadvantage of the material is its ability to release toxic substances during combustion, which are very dangerous to human health. In addition, polystyrene foam is destroyed by exposure to solvents and bitumen-based materials. Expanded polystyrene is a good habitat for rodents (mice, rats, etc.).
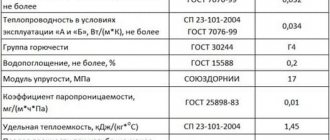
Technical characteristics of PSB-S 35
Expanded polystyrene is produced in the form of rectangular sheets of standard sizes. So, the length varies from 900 to 5000 mm. Moreover, the value increases at intervals of 50 mm. The width is 500-1300 mm (step - 50 mm). The thickness of the material changes in steps of 10 mm and is in the range of 20-500 mm.
Other technical data include:
- Density is in the range of 25.1-35.0 kg/m3.
- The material burns for less than 4 seconds.
- Humidity - up to 12%.
- During the day, the material absorbs no more than 2% of the volume.
- The limiting value of bending strength is 0.25 MPa.
- Ultimate compressive strength - 0.14 MPa.
One of the main parameters that provides a wide range of applications is the ability of foam to retain heat. The thermal conductivity of PSB-S 35 is at a very low level and amounts to no more than 0.038 W/(m*K), which is typical for the dry state.
Terms and GOSTs
According to the old GOST, PSB means pressless polystyrene plate.
In a new way - EPS - expanded polystyrene. Legislation sets standards for all materials used in construction. Until 2014, GOST 15588-86 was in force. Foam sheets produced according to the parameters were given a symbol, for example, “PSB-S-15-900x500x50 GOST 15588-86”.
The decoding means the following:
- P - plate;
- C - from suspension polystyrene;
- B - manufactured using a non-press method;
- C - self-extinguishing, does not support combustion for more than 4 seconds when exposure to open fire ceases;
- 15 — density grade;
- 900x500x50 - geometric dimensions.
To make the foam non-flammable, fire retardants are added to the composition, which is indicated by the letter “C”.
The density grade approximately corresponded to the mass of 1 m3 of foam. For civil engineering, products with a specific gravity of up to 15, 25 and 35 kg/m3 were produced.
The 1986 standard required the maximum weight of the material to be indicated in the name. On January 1, 2014, instead of the outdated document, the new GOST 15588-2014 came into force.
Important amendments for consumers have been made:
- the slabs were named PPS (self-extinguishing polystyrene slabs);
- the specific gravity must now be no less than that indicated in the name.
Some enterprises produce products according to the old GOST and call them PSB boards; the new polystyrene foam is called PPS.
Density characteristics of various grades of PSB
An example of the current designation is PPS16F-R-B-1000x500x120 GOST 15588−2014.
- PPS is a polystyrene board, obtained using a non-press method from a suspension.
- R - cut from large blocks.
- B - with a quarter-size side edge (A - with a rectangular edge).
- 1000x500x120 - geometric dimensions of the slab in mm.
The reasons why manufacturers produce some products according to old standards:
- not all production equipment has been replaced;
- less stringent product requirements that satisfy private developers;
- saving of materials - for example, PSB-S-15 can have a mass from 12 to 15 kg/m3, and PPS-15 is only higher than this value.
The critical technical characteristics of the “old” and “new” slabs do not differ significantly.
Physical and technical properties
If polystyrene foam is properly insulated from environmental influences, it will last more than 50 years.
The popularity of polystyrene foam is directly influenced by technical characteristics:
- thermal conductivity
- density - measured in kg/m3 and indicated in the marking;
- geometric dimensions are reflected in the markings;
- water absorption;
- compressive strength.
The thermal conductivity of thermal insulation boards at a temperature of +10 degrees ranges from 0.036 W/m*K for polystyrene PSB-S-35 to 0.041 for lightweight products PSB-S-15. When the air warms up to 25 degrees, the indicators change slightly - by 1%.
A deviation of 2–5 mm in geometric dimensions is allowed. Tolerances do not affect the quality of insulation, since with such parameters the seams are small and can be easily removed with polyurethane foam.
Water absorption refers to the increase in the mass of foam when it is in water for 24 hours. During this period of time, the foam will absorb from 2 (PSB-35) to 4 (PSB-15)% of liquid from its mass. Thus, polystyrene boards are a moisture-proof material.
Compressive strength will be determined by the areas of application of a particular brand of foam plastic, for example, PSB-15 cannot withstand loads, but polystyrene foam 35 can be walked on carefully.
The service life of foam plastic is limited only by operating conditions - if the sheets are protected from adverse influences, 50 years is not the limit of use.
Advantages and important limitations when using
One person can install polystyrene foam, since the material is light in weight.
The positive properties of the material are determined by the composition and structure of the foam plastic.
In construction the following are important:
- low weight;
- stability of shape and size during temperature fluctuations;
- ease of installation and production of sheets of the required sizes;
- versatility of use;
- long service life;
- resistance to rot and mold, not susceptible to parasites;
- lack of reaction to a slightly alkaline environment (cement);
- non-flammability;
- low thermal conductivity - 5 cm of polystyrene foam retains heat approximately the same as 70 cm of brickwork or 30 cm of wooden beams;
- environmental safety - the finished boards contain about 0.02% styrene, which is released only after heating the foam above 80°C;
- windproof.
The disadvantages are caused by:
- low resistance when exposed to acidic substances;
- destruction from sunlight;
- susceptible to rodent infestation.
Polystyrene of the PSB and PPS grades must be used strictly for its intended purpose and technology, in this case the durability of the insulation is ensured.
Properties of popular insulation
Like many other types of foam, high-density material has similar qualities; it is necessary to list a number of its advantages .
- It has a low level of thermal conductivity due to the fact that it consists mainly of air, so it easily retains heat.
- Resistance to active chemical influences.
- Not afraid of microorganisms, not susceptible to rotting, mold and fungus formation.
- Long service life; with proper choice of insulation and work, it can last about 40 years.
- It is environmentally friendly, so it is used not only in construction, but also in other industries, for example, the food industry.
- New and modern types of material are practically not subject to combustion processes, so they can be classified as fireproof.
- Ease and simplicity of operation, which is very important when performing installation work.
- Low cost of insulation.
New and modern foam plastic is no longer so fragile, since its quality has changed for the better over the years of production. It has become stronger and more durable , so the attitude towards the material has changed.
Production technology
During the production process, foam granules are glued together with pentane and treated with a fire retardant.
In the manufacturing process of the boards, a minimum of components are used:
- polystyrene granules obtained during oil refining;
- pentane - natural gas condensate associated with granule material;
- fire retardant additives that make the material non-flammable;
- water vapor
The production algorithm includes several stages:
- Foaming of raw materials - under the influence of water vapor and pressure, pentane expands in the granules, increasing their volume by 20–70 times. The operation is stopped after the foam balls reach the required diameter.
- Hot air drying.
- Stabilization (tracking) for 4–24 hours. During this time, the balls cool completely and acquire their final size. The pentane remaining in the granules is replaced by air.
- Baking under the influence of hot steam - the balls are sintered into a single product with a volume of several cubic meters.
- Aging (ripening) lasts from one day to 30 days. During this time, the moisture completely evaporates, and the internal stresses in the product are stabilized.
- Cutting to required sizes.
The waste after cutting is ground into individual balls and reused, introducing them at the stabilization stage.
In the final version, the manufacturer receives foamed propylene sheets consisting of 98% air and 2% polypropylene.
Violations of technology do not allow obtaining high quality material.
Equipment for the production of foam plastic can be placed in small workshops. Small firms often produce low-quality products. The parameters are not checked by laboratory methods. You can’t rely on a low price when purchasing.
Methods of use
Foam plastic is used for thermal insulation of houses outside, as well as refrigerated rooms for storing food.
GOST provides for the use of foam plastic sheets for thermal insulation:
- external walls of existing and newly constructed buildings and structures;
- individual premises and industrial equipment, in the absence of contact between the slabs and the volume of the internal premises;
- refrigeration chambers at temperatures from –100 to +80°C;
Foam plastic is suitable for “wet” façade systems. It is used as a middle layer in panel structures.
Appendix A to GOST indicates the scope of application of foam plastic grades depending on density. PSB-S-15 or PPS grades from 10 to 15 are recommended for unloaded thermal insulation in three-layer structures made using ventilated facade technology. PSB-S-25, PPS 16-20 are suitable for external walls for finishing with cement and composite plasters. The material of this brand is suitable for insulating floors under screed, ceilings, and roofs. PSB-S-35, or grade PPS 20 and higher, is used for an insulating layer under cement screed, for surfaces under the influence of significant loads - paths, blind areas, foundations and plinths of buildings for various purposes.
Scope of application of expanded polystyrene 35
Insulation is widely used:
- For the production of permanent formwork.
- For thermal insulation of basement and ground floors (filled with concrete with sheathing).
- For insulation of roofs of buildings and structures.
- For strengthening slopes, draining wastewater, preventing swelling and freezing of soil during the construction of swimming pools and sports fields, as well as when laying out lawns.
- In addition, PSB-S 35 foam is used for the manufacture of multilayer panels.
Insulation of the foundation and floor
In most cases, foam plastic is actively used as a middle layer in three-layer foundation blocks.
Using the same principle, it can be placed in a sandwich panel. When creating formwork, the material takes on the function of permanent formwork if the foundation is created directly at the construction site.
Thanks to this, the consumption of concrete mass, reinforcing bars and the total amount of labor costs is significantly reduced.
Polystyrene foam can be used as an excellent thermal insulator in foundations to prevent them from freezing.
The fact is that such thermal protection is especially relevant in the northern regions of the country. In addition, the product can be used in the construction of basement-free premises.
To do this, insulating slabs are laid on a pre-prepared site, which are then poured with concrete.
After this, the building is completed using the usual method. In such a structure, the concrete screed serves as the foundation and base of the floor.
Foam plastic (expanded polystyrene) sheet PSB-S-35
Extruded polystyrene foam boards can be used to create vertical and horizontal protection of the foundation from deep freezing.
In order to organize this, you need to dig a trench with a width of 1 meter and a depth equal to the level of soil freezing. Thermal insulation slabs are laid along the entire foundation, after which they can be covered with soil.
Sometimes it is necessary to form an additional waterproofing layer. When insulating floors, polystyrene foam boards are also used, which serve as a thermal insulation coating.
In addition, they prevent the transmission of impact noise, such as loud footsteps or moving furniture. To do this, foam plastic boards with a thickness of 50 millimeters are laid on top of a layer of material with insulating properties.
After sealing the seams is completed, a bridging slab made using wood chips is placed on top. An alternative is a mixture of sand and cement with a layer thickness of 6 centimeters
Roof insulation
A cold attic or attic can be insulated with polystyrene foam in the shortest possible time. To do this, before starting the main work, you will need to attach the sheathing from below to the rafters - the foam plates will subsequently rest on it.
The thickness of the insulating layer should not be less than 100 millimeters. If two layers of polystyrene foam are formed, the rafters will need to be additionally built up, since otherwise it will be problematic to secure the sheets.
The foam is laid between the rafters from the inside. It is important to maintain the distance between individual slabs - it should not exceed 10 millimeters.
If large gaps are left during the installation process, then during the shrinkage of the house, the slabs may collide with each other and become deformed.
If during the installation process gaps appear between the slabs, they will need to be carefully sealed. For this, in most cases, ordinary polyurethane foam is used, which is applied using a construction gun under high pressure.
Expanded polystyrene ready for packaging
Insulation boards are attached using wooden slats or glue. Experts recommend using the method of gluing slabs.
You can also use dowels or nails for strengthening, since over time the adhesive composition may lose its original properties.
The attic floor must also be thermally insulated. To do this, it is cleared of accumulated debris and elements of outdated backfill.
After this, a vapor barrier layer is laid. Expanded polystyrene slabs are placed on the surface of the ceiling, and all resulting joints are sealed using polyurethane foam.
If the attic will subsequently become a living space, then a covering must be laid on top of the insulating layer that can easily withstand the weight of people moving through it. This can be a boardwalk covered with hard linoleum or parquet.
Review of polystyrene foam PSB S 35 (video)
Features of the pressless production method
When using the pressless method, ready-made polystyrene granules are used as raw materials. PSB insulation is produced as follows. When heated to a temperature of 80°C, they acquire a viscous-fluid state, after which the flammable hydrocarbon isopentane is supplied. It boils at a temperature of 28°C, simultaneously foaming polystyrene granules.
After foaming, the granules come into contact with water at a temperature of 90-100°C and are welded together. The finished product usually leaves the production line in the form of a parallelepiped, after which it is cut into slabs of specified sizes using heated nichrome wire.
Installation features and tips for buyers
1. If you decide to purchase PSB-S 35, you should not take it from open storage areas. Unexposed polystyrene foam is white and free of stains and faded areas. Its balls are approximately equal in diameter, and the entire slab is both elastic and soft.
2. When choosing, the sheets must be placed side by side and compared: all characteristics, length, width, and especially thickness must be respectively identical to each other. On the foam itself there is a marking for decoding.
3. There are several features during installation. Thus, the work is carried out on leveled walls, coated with an antifungal primer. After drying, glue is applied to them and insulation is installed. The seams between three sheets of polystyrene foam should be T-shaped (masonry bonding). To completely harden the PSB-S binder, leave it alone for a couple of days.
4. Then, if the joints are more than 4 cm wide, then they are sealed with strips of polystyrene foam with the same characteristics; if less, then with polyurethane foam followed by gluing. Holes are drilled through the foam in the wall for plastic dowels, which are driven in there. In turn, plastic nails with a very large head are driven into them. Their goal is to make the connection more reliable.
5. Next, a reinforcing mesh is glued onto the polystyrene foam, so that it does not protrude anywhere from under the fastening agent. The dried glue is smoothed with sandpaper, the surface is puttied and primed for wallpaper, paint or other coating.
Cost of PSB-S 35
For all calculations, such as prices per sheet, square meter, entire insulated surface, the basis is the cost of 1 m3 of polystyrene foam. It depends on the density, since the production of different brands will not require the same amount of raw materials, board parameters, location and volume of delivery, and prices for the use of transport. In addition, each manufacturer and seller may have different financial policies. Most often, the price fluctuates throughout the country in the range of 3200-4000 rubles per 1 m3.
Knowing the dimensions of the slab and the cost per unit volume, it is easy to calculate how much the required amount of polystyrene foam will cost. For example, for 3200 rub/m3:
| Parameters of sheet PSB-S 35, (mm) | Thickness, mm | Pieces per 1 m3 | Panel price, rubles |
| 1000x1000 | 200 | 5 | 640 |
| 190 | 5,26 | 610 | |
| 180 | 5,55 | 580 | |
| 170 | 5,88 | 540 | |
| 160 | 6,25 | 510 | |
| 150 | 6,66 | 480 | |
| 140 | 7,14 | 450 | |
| 130 | 7,69 | 420 | |
| 120 | 8,33 | 380 | |
| 110 | 9 | 350 | |
| 100 | 10 | 320 | |
| 90 | 11,1 | 290 | |
| 80 | 12,5 | 260 | |
| 70 | 14,28 | 220 | |
| 60 | 16,66 | 190 | |
| 50 | 20 | 160 | |
| 40 | 25 | 130 | |
| 30 | 33,3 | 96 | |
| 20 | 50 | 64 |
Conclusion: instead of two layers of, say, a 60 mm panel, you can lay PSB-S 35 foam plastic with a thickness of 120 mm, and vice versa.
Methods of working with foam plastic
Polystyrene foam is afraid of sunlight, so after installation it is insulated with a protective layer.
When choosing a method and technology of insulation, take into account the requirements of GOST and common sense:
- The foam must be protected from ultraviolet radiation - direct sunlight.
- Impact loads on the surface are excluded; it must be protected from physical impact.
- Sheets should not be exposed in the interior of the premises due to possible damage and styrene fumes.
Foam insulation in private construction is carried out using the technologies of a ventilated facade, a “wet” facade under plaster, and laying between layers of enclosing material.
Finishing procedure for plastering
To insulate facades, a special adhesive for foam plastic is used.
For work, choose PSB-S-25, or PPS-16F. It is impossible to use foam with a lower density as it will not withstand the mass of cement mortar. Buying expanded polystyrene boards with a specific gravity of 35 kg/m3 does not make sense - the material in all respects is not inferior to models 15 and 25, but is much more expensive.
Warming algorithm:
- Walls made of brick or expanded clay concrete (foam concrete) blocks are cleaned of dust and dirt stains.
- The surface is leveled, knocking down the influx of masonry mortar. If necessary, plaster - it is important that there are no differences of more than 1 cm per linear meter of the wall.
- Prepare a solution from a special glue for cement-based polystyrene.
- The glue is applied to the slab in a layer of 0.5–1 cm and leveled with a notched trowel.
- Glue the PSB to the wall, laying the sheets in a checkerboard pattern. Another option is to use foam adhesive.
- For reliable fastening, after 3-4 hours, polystyrene slabs are additionally reinforced with dowels with wide heads at the rate of 5 dowels per m2. Seal the joints with polyurethane foam.
- The first layer of plaster is applied, for which the same glue is used that was used in step 4. The plaster mesh is pressed into the layer of plaster and the surface is leveled.
- After drying, basic plastering and puttying are carried out or decorative mixtures are used, for example, bark beetle.
- Paint the surface.
Wet facade technology is rarely used for wooden houses. It is believed that foam plastic does not allow air to pass through and the house stops “breathing”; fungus and mold appear on the inner surface of the walls. The issue can be resolved by properly organized ventilation of the premises.
Insulation of hollow brick walls
Polystyrene foam can be laid between two brick walls.
The technology is simple. Between the internal load-bearing walls and the external finishing bricks, cavities are left into which polystyrene sheets are laid as the masonry is being built.
They use the cheapest version of polystyrene foam PSB-15. The load in the wall cavity is completely absent, and the characteristics of the material are not inferior to polystyrene foam with a higher density.
When filling hollow walls, it is more profitable to use foam chips - it is cheaper and allows you to completely fill the internal space between the bricks. The material is sold in kraft bags with a volume of 1 m3.
Frame houses and foam plastic
A popular insulation material for the construction of frame houses is foamed polystyrene.
Polystyrene foam is installed between the inner and outer skins. The gaps between the PSB and the beams are sealed with polyurethane foam; this will eliminate “cold bridges” and prevent the wind from blowing through the structure.
It is important to leave ventilation gaps between the foam and the wall sheathing to prevent moisture from accumulating inside.
Conclusion
Polystyrene foam of this brand is a material of optimal density, it is durable and is not susceptible to destruction over a long period of time. It is believed that this brand is the most “warm”; its reputation has been justified for more than one decade. Its acquisition is quite profitable, since it is widely used in various fields of construction.
Sources
- https://feroteks.ru/info/penoplast-psb-s/psb-s-35/
- https://FB.ru/article/314561/tehnicheskie-harakteristiki-psb-s-teploizolyatsiya-sten-penopolistirolom-psb-s
- https://StrojDvor.ru/otoplenie/universalnyj-teploizolyacionnyj-material-psb/
- https://uteplimvse.ru/vidy/polistirol/psb-s-35.html
- https://obogrevguru.ru/penopolistirolnye-plity-marki-psb-s-35.html
- https://kotel.guru/uteplenie/utepliteli/harakteristiki-penoplasta-psb-s-35-plotnosti.html
[collapse]