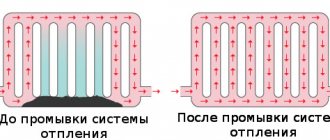
Replacing piping is an expensive option for improving your heating system. High-quality flushing of the system allows you to eliminate various contaminations of pipes, which lead to a significant reduction in the heating temperature of heating equipment.
Pipes before and after flushing.
High fuel consumption and low heating temperature of the heating system are the most important indicators of the need to clean the system.
- 2 Methods for performing work on flushing heating systems
- 3 Features of registration of the washing report
Procedure for registration and work
The instructions for a flushing organization look something like this:
- The equipment is pre-inspected
. Its technical condition is assessed and initial pressure testing is carried out with a pressure exceeding the working one by 1.25 times, but not less than 2 atmospheres. What is it for? So that leaks that appear during the work do not become a reason for conflict with the customer. Identified malfunctions are eliminated before flushing begins. - An act is drawn up for hidden operations during the execution of work
. Let's say on ; for disconnecting flanges for connecting a chemical flushing pump, etc. - The technology for cleaning the heating system is selected
. In the vast majority of cases, hydropneumatic flushing is used using a slurry of water and compressed air; less often - chemical cleaning. - An estimate is drawn up for flushing the heating system
. The total cost includes the cost of depreciation of equipment, fuel consumption, reagents and payment for the actual work, including hidden ones. - Based on the estimate, a contract for flushing the heating system is drawn up
.It stipulates:- Cost of work and procedure for calculating cost.
- Obligations of the parties, including deadlines for completing work.
- After signing, the actual work is carried out
. - After washing, a secondary wash is carried out
. The system is checked for functionality. - Upon completion of all work, a heating system flushing certificate form is filled out
. The customer evaluates the quality of the work and accepts it or declares non-fulfillment of the terms of the contract.
Controversial issues are resolved in the prescribed manner through the courts.
Standards
Before pressure testing, a special program is drawn up, which is approved by the engineer of the heat supply organization. It should define:
- Sequence of work.
- Personnel procedures.
In addition, it is indicated which team will perform the work and which teams are working in adjacent areas. Pressure testing of heating equipment is carried out under the supervision of the shift supervisor. In this case, all other work aimed at repairing or maintaining the pipeline must be stopped. Do not remain in the immediate vicinity of the equipment under test when the pressure rises to the maximum value. Inspection of pipes and other heating equipment should be carried out only at average values. If work is carried out in areas adjacent to the test subject, they must be fenced off and disconnected from the test equipment. If the inspection was carried out in compliance with all the above standards, an act is signed, which will be discussed below.
When the system should be cleaned
The system will require an initial flush after installation to remove any remaining flux or pipe joining material, as well as any metal particles such as swarf left over from recent installation or changes to the piping.
If the system is properly maintained, well designed, and regularly treated with a corrosion inhibitor, unscheduled flushing is unlikely to be required unless significant changes are made to the system.
However, not all of these requirements are common and sludge can build up in the system very quickly. Here are a few clues that indicate that sludge has already begun to accumulate in the heating system:
- cold “spots” on the bottom of radiators;
- parts of the heating circuit that do not heat up correctly;
- Excessive noise (bumps, clicks, pops) made by the boiler when it heats up.
The heating circuit should also be thoroughly flushed before installing a new high-efficiency condensing boiler, as the heat exchangers in such boilers are particularly susceptible to damage from contaminants in the heating system.
General information
Before cleaning, you should check the system to determine its configuration. You also need to determine the “age” and general condition of the components in order to select the required system flushing mode. For example, the procedure may remove corrosive debris blocking openings in radiators, which can lead to coolant leaks. If there is any doubt as to whether the system will withstand any cleaning methodology, replacement or repair of the relevant components will be required before proceeding.
Cleaning procedure
There are several ways to clean a system and there are a number of cleaning products on the market designed to help flush heating systems. Many products are designed to be added to the circulating water some time before flushing and help mobilize contaminants prior to flushing. Here you need to follow the instructions from the manufacturer of these products.
Basic flushing procedures:
- Powerflushing.
- Overpressure flushing.
- Flushing with a circulation pump
Positive pressure flushing is probably the most effective procedure (although it is important to check the boiler manufacturer's instructions to determine whether flushing the system using the boiler in the heating circuit is acceptable). Powerflushing is also an effective method for cleaning heating systems, especially those containing high levels of black magnetite sludge.
Powerflushing is also an effective method for cleaning heating systems, especially those containing high levels of black magnetite sludge.
Please note that with all methods, changing the direction of coolant flow will help remove debris that could otherwise remain in the system and cause it to fail.
Preparation
Before flushing with any method, there are several general preparation steps. Typically these involve adding a suitable detergent to a running heating system and letting it sit for some time before actually flushing. The cleaner is usually flushed (while hot) from the system and the system is primed to begin the final flushing process.
Before flushing, you may also need:
- Turn off all electrical controls and electrically isolate the system.
- Avoid supplying cold water to the central heating system.
- Manually close all heating circuit vents.
- For systems with open ventilation, close or temporarily connect the open ventilation and cold water supply to the supply and expansion tanks.
- When draining a vented system, the collection tank may have quite a large portion of floating sludge. It must be removed to prevent it from being drawn into the pipeline.
- Mark the operating position of any shut-off valves or other control valves, and then open all valves fully.
- Remove all thermostatic radiator valve (TRV) heads to ensure maximum flow through the valves.
- Set any diverter or zone valves to their manual open position.
- Where check valves are present, they must be closed, bypassed or temporarily removed, otherwise this will prevent flow reversal.
Heat supply flushing methods
It is not recommended to start flushing the heating system without preliminary preparation. It is necessary to determine the chemical composition of scale and select a specific type of equipment for cleaning.
A technological map that prescribes all stages of the procedure will help you correctly complete the necessary steps. The latest regulation ends with the treatment of the internal area of the pipes with a chemical composition to prevent the appearance of corrosion, lime deposits, and scale.
The main washing methods are the following:
- chemical method;
- hydrodynamic;
- hydropneumatic.
Chemical flushing of coolant
This method does not involve the intervention of mechanical devices and the dismantling of radiators. Cleaning is carried out with chemicals or solutions.
However, using the method can damage the inner plane of aluminum radiators, which can lead to their destruction.
If the heating network is not very clogged, you can use the following reagents:
- sodium hydroxide;
- vinegar essence;
- ordinary phosphoric or condensed acid;
- whey.
However, it is better to use compounds that allow you to thoroughly clean the pipes. The instructions for the preparations specify the material and the nature of the layers.
Chemical treatment can be carried out using additional equipment - a booster, consisting of a centrifugal pump and a large container. The first one is connected at the break in the centralized supply system with the heating boiler. A valve must be installed at the outlet of the circuit to discharge the spent chemical.
For high-quality corrosion of lime deposits, experts recommend leaving the reagent in the network for several days, depending on its slagging level. However, to avoid exposure of the pipes to the chemical, the circuit must be rinsed with industrial or tap water after cleaning.
A more gentle metal structure is the dispersed cleaning mode. The method differs from the chemical method in that the reagent destroys the mechanical bonds of the deposits themselves, without interacting with the material of the heating communications.
Hydrodynamic cleaning
The described operation is carried out using specialized equipment. One of them is a powerful centrifugal pump with a hose having a small diameter end nozzle. Strong water pressure cleans scale and deposits from the walls of heating mains and removes them through the return line.
Mechanical flushing method
Method for cleaning radiators and small pipes. The shut-off valves, expansion tank and centrifugal pump must be cleaned separately. Before the procedure, it is necessary to carry out a minimal drain of the house system, and then close the inlet and drain valves. Only after this they begin to reset the rest of the media.
The discharge occurs through a drain valve installed in the basement, which communicates with the sewer through a hose. This will prevent the technical subfloor from flooding with water. Radiators are cleaned by unscrewing the plug and dumping the media. However, removing the battery and processing will improve the thermal performance of the radiator.
After dismantling the radiators and areas of heating distribution to the yard, the equipment is cleaned with a cable with a brush-shaped tip. The tool is inserted into the batteries in the reverse position to the supply of thermal resources to improve the removal of scale flakes and deposits. Cleaning is carried out until the rinsing water becomes clear.
Hydropneumatic
Belongs to an effective and equipment-friendly method for cleaning heating circuits. Contains a high pressure air jet. The compressor creates high-power turbulent flows inside the communications, leading to the breakdown of build-ups and washing out accumulated dirt.
The operation is performed with a pneumatic gun that delivers short-term impulses. Lime deposits are discharged through open radiator plugs. The initial purge procedure is performed against the flow of the coolant, and the repeat procedure is performed clockwise. Removing batteries and cleaning them outside will improve air operations.
Electrohydropulse cleaning option
The method is based on the formation of an electric discharge, the shock wave of which breaks up lime deposits on the internal walls of the system, without causing harm to the latter. To carry out cleaning, you will need a voltage generator and a coaxial cable to supply high-frequency signals.
The efficiency of the method is high, so the dismantling of radiators and the entire heating circuit is not provided. After the scale is destroyed, the coolant is washed and the water goes down the drain.
Features of dismountable flushing of the heat exchanger
If the heat exchanger is very dirty or completely out of order, dismountable flushing can help. The rules and technology for dismountable washing are quite simple. It is necessary to disassemble the heat exchanger, remove all the plates, soak them in a special solution, wash each plate manually, and insert the package of plates into the heat exchanger. After this, the heat exchanger is assembled and pressure tested.
By following the rules of this work, you will receive many benefits:
- dismountable heating flushing guarantees the highest quality;
- any contamination is eliminated;
- everything happens clearly, and you can see the entire work process.
However, there are also disadvantages that cannot be avoided, even if you follow all the rules of work. So, if your heat exchanger has been worn out, under critical conditions, or the service life of the rubber seals has expired, then you may have to change the heat exchanger seals, which will increase the cost and duration of the work.
- in the case of dismountable washing, it is sometimes possible to remove contaminants using a jet of water from a special high-pressure apparatus;
- If there are more serious deposits, you must first clean the heat exchanger plates from the top layer of deposits using a high-pressure apparatus, then soak them in an acid solution, and then clean them again using a high-pressure apparatus.
Options for flushing heating systems
The choice of cleaning method depends on the total length of the circuits, the degree of contamination and other factors. Methods include:
- Mechanical method.
- Hydrochemical cleaning.
- Hydrodynamic flushing.
- Electrohydropulse method.
- Hydropneumatic option.
Washing Process
Some methods require equipment. Hydropneumatic guns can be rented, but you will need some skill to operate them.
There are a number of general rules for flushing the heating system of a private or apartment building. If you deviate from their implementation, efficiency will be low.
Mechanical cleaning
The method is suitable for cleaning batteries. All other elements will have to be cleaned separately. First you need to drain the coolant from the system. You must first close all valves that limit the flow of coolant into the radiator. In high-rise buildings, valves are usually located in the basement, in private houses - on parts of the circuit before and after the heating element.
Mechanical cleaning
To drain the liquid, you need to open the drain valve located on the circuit. If it is missing, it is enough to unscrew the plugs on the last battery located below the others.
It is convenient to discharge the coolant through a hose that is connected to the tap and discharged into the sewer. The mechanical cleaning method is effective when the heating elements are first removed and the pipes and radiators are cleaned separately.
The dismantling method depends on the connection options and other parameters. It is necessary to protect the floor from flooding by placing a container. Take the radiator outside or into the bathroom (the enamel parts must be protected with a rag). To prevent clogging of the sewer, it is necessary to block the drain in the sink with a network.
After mechanical cleaning, it is necessary to rinse the pipes with plain water. Through a water tap or hose, supply water under pressure into the radiator. Rinsing is carried out until the water becomes clear.
Hydrodynamic cleaning
The method involves supplying water to the circuit from a pump under high pressure. Can be connected to an open circuit to use as many radiators as possible before the water is discharged. However, special hoses are used for this.
Hydrodynamic flushing principle
For small deposits, pressurized water effectively counteracts salts and dirt. You will have to rinse several times. After cleaning, the operation of the heating system will improve significantly.
Chemical washing method
The principle of the method is based on the introduction into the cavity of the radiator of substances that dissolve or promote the peeling of scale. They use both ready-made substances and solutions prepared with their own hands. It may not be necessary to remove radiators from brackets.
However, it is prohibited to wash aluminum radiators. Caustic solutions are formed that cannot be poured down the drain.
To clean lightly dirty circuits, it is enough to:
- Soda;
- Vinegar;
- Acid.
It is better to use special compounds. After finishing work with chemicals, it is necessary to flush the pipes.
Dry cleaning
Hydropneumatic flushing
This cleaning method involves treating internal surfaces with an emulsion under high pressure. Emulsion is a mixture of water and oxygen. The effectiveness of the method is high, however, sophisticated equipment is required.
Suitable for cast iron radiators with large collector capacity. There are no strict requirements for the type or material of elements. The method is quite expensive, but is compensated by its effectiveness and safety. To reduce the impact on batteries, pre-treatment with chemicals is necessary.
Hydropneumatic
Electrohydropulse technique
The principle of operation of the method is to use an electrical pulse that destroys insoluble substances that transmit current.
To create an impulse of this level you need a special apparatus. A coaxial cord is connected to it, on which a charge is formed; the shock wave destroys scale on the surface of pipes or radiators. After cleaning, you need to rinse the system with clean water.
Electrohydropulse washing, results
This method is effective and does not require complete disassembly of the system. However, equipment is required. Slag waste can be washed down the drain.
Certificate of pneumatic testing of pipelines
Pneumatic method: diagnosis by pumping the system with high pressure air. Often the method is used for external systems if the temperature on the thermometer is less than +5 Celsius.
Requirements for drawing up test documentation:
- Filling in the name of the city and the date of compilation.
- Indication of the members of the commission (as in the hydraulic test, three parties are involved).
- Description of the pipeline: length, diameter, material of pipes and joints.
- Information about the pressure value: calculated value, to what value the pressure in the pipes was increased, final pressure, amount of reduction. The crimping time is indicated.
- In the “Decision of the Commission” section, each of its members signs with a transcript if the pipeline has passed pneumatic diagnostics and is sealed and durable.
Causes of clogged heating pipes
The water contains many additional components. The most predominant are iron, calcium and magnesium. When exposed to relatively high temperatures, they are released in the form of small fractions that settle on the inner surface of pipes and radiators.
Therefore, before washing aluminum radiators, you need to find out the nature of the contamination. In addition to calcium and magnesium deposits, oxide deposits can form due to natural rusting of metal heating components. Depending on the nature of the contamination, the optimal cleaning technology is selected.
Usually the plaque includes the following elements:
- Iron oxides. In a system with steel pipelines and radiators, they can occupy up to 25% of the total plaque volume;
- Calcium and magnesium deposits occupy up to 60%;
- Oxides of copper, sulfur and zinc – up to 15%.
Since the heating radiator in an apartment should be flushed only after a preliminary analysis of the nature of the contamination, it is recommended to first take a plaque sample. To do this, you can dismantle part of the pipeline. In practice, this is not always done, especially for heating systems installed relatively recently.
Stages of preparation and carrying out crimping
Before starting preventive manipulations, the master determines the features of the system. The calculation is needed to supply the standard pressure, since exceeding the indicator will damage the heating equipment.
Indicators taken into account:
- type of wiring;
- characteristics of the pipeline - material, wall thickness, degree of wear;
- number of storeys of the building;
- features of shut-off valves.
Upon completion of the calculations, the specialist will pressurize the network.
Stages of work:
- Preparation of equipment for injection of water or air.
- Disconnecting the network from the coolant supply. This is required during the heating season if equipment was repaired after a pipe or battery burst.
- Draining coolant from the main.
- Injection of test substance under pressure. Maintaining the design high pressure for a certain period of time.
- Draining the test coolant, flushing the system, filling with standard substance.
After the test, a crimping certificate is issued. Defects identified during prevention should be eliminated. The absence of leaks means the line is ready for continuous operation.
Why do you need to flush your heating system?
The water that flows through the heating pipes is far from distilled. What it doesn't have:
- mechanical impurities: rust, sand, scale and other dirt;
- chemical impurities: metal salts, especially calcium and magnesium;
- microbubbles of dissolved air and other gases.
Coupled with temperatures up to 100°C and high pressure, all this forms a “hellish” mixture. Chemical reactions take place around the clock, the main result of which is the formation of scale, corrosion of heat exchangers and communications.
The water entering the system must not only be filtered from mechanical impurities, but also brought to the required chemical and physical characteristics, that is, meet the standards for water treatment in thermal systems.
If measures are not taken in a timely manner:
- the heat transfer of the system is noticeably reduced;
- energy consumption increases;
- The walls of the pipes and boiler become thinner and destroyed, and leaks form in various elements of the pipeline.
There are several ways to remove harmful deposits. Of these, hydropneumatic flushing of the heating system is the most radical and effective. It is used both in private and multi-storey buildings.
Why is system pressure testing used?
The heating system has natural or forced circulation of coolant. In forced systems, the liquid moves through pipes using a pump; in natural systems, it is supported by a certain pressure in the circuit. Pressure testing - checking the tightness of all connections. It is performed immediately after installation of the system before commissioning, as well as after a period of downtime in the off-season, repair, redevelopment and modernization of system elements.
Pressurized water or compressed air is supplied to the heating system circuit. This procedure allows you to identify weak points in the circuit, poor-quality connections, and leakage points. Damaged elements and places with poor-quality connections leak. Thus, it is possible to quickly and efficiently eliminate malfunctions before starting the system. Checking for leaks prevents circuit breakage and leakage during sudden pressure changes in the heating system.
Regulatory Standards
To properly carry out pressure testing of networks, you need to know the regulatory framework. This knowledge is also important when carrying out design and installation work.
The main recommendations for conducting hydraulic tests are listed in SNiP number 41-01-2003:
- when carrying out test work in the structure, the temperature must be maintained at least zero degrees;
- when determining the crimping pressure, adhere to the data on the maximum permissible pressure that the materials and equipment used can withstand (the crimping pressure should not exceed the limit values);
- the pressure in the system during testing must exceed the performance indicators of the equipment and materials used by 50% (however, this value cannot be less than 0.6 MPa).
Another regulatory document (SNiP number 3.05.01-85) contains the following information:
- All large-unit elements can only be tested at the assembly site.
- If during testing the pressure in the system drops, then you need to inspect the entire line and instruments to identify the location of the leak. After this, repair work must be carried out to eliminate the leak. Then activities to check the tightness of the networks continue.
- If wedge valves and valves are installed on the main line, then pressure testing can be carried out by turning the control handle twice.
- If non-factory assembled devices are used in the circuit, they are crimped on site.
- If hidden piping is used in the house, then these areas are pressurized before finishing work is carried out.
- Pipelines that must be insulated are checked for leaks before installing thermal insulation material.
- During testing, membrane tanks and hot water boilers must be turned off.
- The heating system is considered working if the pressure test does not decrease within half an hour, and if it is not possible to visually detect leaks.
- Additionally, the heating circuit is checked for uniformity and correct heating. To do this, the network supplies coolant with a temperature of at least 60°C for 7 hours.
Is it possible to wash a separate battery?
Now you know how to flush the heating system. However, sometimes it becomes necessary to clean a separate battery. There is a solution for this situation too.
Buy a flushing faucet from a plumbing store. Additionally, you need to purchase a rubber hose and a fitting with a thread that matches the diameter of the purchased flushing valve. Install the fitting onto the hose.
Direct washing is carried out in the following sequence.
First step. We connect the flushing tap to the heating radiator.
Second step. We connect a fitting with a hose to the flushing tap.
Third step. We direct the second end of the rubber hose into the toilet.
Fourth step. Open the flush tap and leave for 20-30 minutes. While waiting, hold the hose so that it does not jump out of the toilet.
Additional work
After washing pipes and other equipment, it is advisable to perform pressure testing. This additional procedure will allow you to check the tightness of the entire system and identify places where air or water may escape. Such actions are not mandatory, but highly desirable. They correspond to the interests of both the customer and the contractor. Upon completion, both will be able to verify the quality of the previous stage. The completion of the work is recorded by the act of flushing and pressure testing the heating system. A sample of it will look like a table that contains a list of all activities carried out during such a procedure.
Against each of the points, the specialist must make a note of completion. At the end, as usual, the customer and the contractor put their signatures, confirming the fact of the work. Experts sometimes call this procedure a hydraulic test, since most often such a test is carried out using water. It is believed that the air may be more dangerous when serious faults are detected. Therefore, many people prefer to take the easier path.
In what cases is the act filled out?
The document is required at the time of acceptance of gas, heat and water supply. We are talking about both a newly opened system and one that has undergone repairs or scheduled maintenance. The most common type of pressure testing is hydraulic testing of the water supply system. The entire set of tests is designed in such a way as to check the operation of the system under various conditions.
After filling out the form, you should check it
The operator evaluates how the degree of tightness of the entire pipeline changes. During hydrotesting, not only the tightness is tested, but also the quality of the existing joints. In most cases, they are the cause of failure of a separate section. In addition to the pipeline, terminal equipment is subject to control. The heating system installed at the consumer's place, taps and gas stoves - all this needs to be checked.
Each stage of control is regulated by a separate SNiP:
- 41-01-2003;
- 3.05.01-85;
- Rules for technical operation of thermal power plants.
The regulations for conducting hydrostatic testing are prescribed in several regulations. They regulate the order and timing of tests. Consumers of utility services should remember that compliance with these deadlines is in their interests. Preventive examinations allow you to detect problems at an early stage.
Procedure for cleaning pipes yourself
To clean the heating system pipes with your own hands using chemicals, you need to know how to flush the heating system and follow a certain sequence of actions:
- The system must first be thoroughly examined to determine which solution to use for cleaning.
- Next, carefully study the instructions for the selected chemical. The solution must be prepared in strict accordance with the specified recommendations, since each preparation has a certain consistency.
- Fill the pump reservoir with the prepared solution and connect the device to the system.
- It is necessary to ensure that the chemical is moving through the system.
- Wait a certain period of time, which depends on the degree of contamination and its composition.
- At the end of flushing, remove the chemical solution from the system, rinse it thoroughly and fill it with clean water.
Peculiarities
Flushing the heating system cannot be done “blindly”, because you need to know what you will encounter. Typically, batteries do not heat up well when the fluid circulation in them is weak due to debris clogging the internal walls. It is found in the water itself in the form of suspensions of alkali salts, heavy metals and rust. Utilities are required to flush the system annually to prevent a decrease in water flow. But often this task has to be performed by the residents themselves, inviting specialists to clean the radiators from the dirt compacted inside.
This problem is especially typical for cast iron batteries, where sometimes there is a channel for water circulation no more than 1 cm in diameter due to infrequent washing. The cause of clogging of steel radiators is stagnation of rust, due to which they are subject to not only clogging, but also destruction. Not every type of flushing is suitable for such batteries, since after some methods leaks may appear in them. Plastic radiators also become clogged, but cleaning them differs from cleaning their metal counterparts.
This process cannot be called universal, because it is selected specifically for each case. An example of a bad choice is the flushing of the heating system by housing and communal services workers, when they apply powerful pressure by abruptly opening the riser valve located in the basement of an apartment building. This leads to knockout of locking elements and leaks at the junctions of spans. But not every family owner can disassemble the battery into separate bends for the purpose of mechanical cleaning in order to solve the problem of a clogged heating system.
When flushing radiators in an apartment on the lower floors, one cannot always expect the efficiency of the coolant, since for high-quality cleaning it is necessary that the neighbors of all floors of the same branch do the flushing. Otherwise, after cleaning one apartment and washing the batteries by utility workers with high pressure, some of the garbage may fall behind the walls, and mud masses will fall into the newly cleaned batteries. However, it is unlikely that all neighbors will agree when it comes to flushing, but the insufficient internal cross-section creates high hydraulic resistance.
Every mm in thickness of deposits increases fuel consumption by 20-25%. In central heating systems, the water must be pre-treated to reduce clogging. But this is not always done, although residents pay decent amounts every month for house maintenance. In addition, radiators last for decades without replacement. According to the established regulations, flushing of centralized and autonomous systems must be carried out annually. This period is critical. If the pipes are not flushed before the start of the heating season, the pipeline becomes clogged, causing the heating equipment to break down.
If you ignore the blockage, the consequences can be disastrous:
- the heating system may freeze;
- you will have to buy new batteries;
- You will need an electric heater, which will increase the price of electricity.
Unauthorized coolant discharge
For unauthorized draining of the heating system, the violator faces administrative punishment. The fine is 10,000-15,000 rubles, as stated in Article 7.19 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. In addition to the sanctions, you will need to pay a penalty of more than 170,000 rubles to the heating network.
Flushing of the housing construction circuit occurs annually after the end of the heating season. Before cleaning, the equipment is analyzed and a treatment method is selected, which will improve the heat transfer of apartment radiators.
Watch the video: “Do I need to drain the water from the heating system in the summer?”
What else to read:
- Detailed instructions for calculating subsidies for housing and communal services in 2022 - online calculator
- How to apply for and receive a subsidy to pay for housing and communal services in 2022 for pensioners, low-income people, veterans, families with many children through the MFC, GosGosuslugi and telephone
- Standards for the temperature of hot water in the tap of an apartment in an apartment building in 2022 - standards according to SNiP, SanPin, GOST, recalculation and sample complaints
Concentrates
DIXIS LUX
The drug is diluted with water (preferably soft or rain) in a ratio of 1 to 9. The product is suitable for heat transfer surfaces made of ferrous metal, stainless steel, and copper alloys.
Price: from 1530 rub./10 l.
DIXIS LUX
pros
- low price;
- neutralizing solution included;
- You can drain the used product into the sewer;
- quick rinse (2.5 hours);
- Contains only organic acids, acid corrosion inhibitor.
Minuses
the required temperature of the working environment is 60...70 °C.
DIXIS LUX
ARGUS SUPER POWER
Before use, the concentrate should be diluted with 10-15 liters of water, depending on the degree of contamination. Contains a corrosion inhibitor. Operating temperature for effective cleaning is 20...40 °C.
Price: from 1200 rub./4 l.
ARGUS SUPER POWER
pros
- low cost;
- color indicators;
- corrosion inhibitors;
- low operating temperature.
Minuses
- has a characteristic odor;
- there is no information about the possibility of draining liquid into the sewer.
ARGUS SUPER POWER
Heat Guardex Cleaner 824R
The product is intended for cleaning the circuit in a heating system running on antifreeze. The product is diluted in a ratio of 1 to 30.
Price: 6400 rub./l.
Heat Guardex Cleaner 824R
pros
- highly concentrated substance;
- Effectively removes sludge and glycol residues.
Minuses
high price.
Heat Guardex Cleaner 824R
TELAKKA HEAT
1 liter of concentrate is diluted in 3–5 liters of water. The product is suitable for flushing systems with plastic and rubber tubes. The product is safe for sealants. The working temperature of the solution is 20...35 °C.
Price: from 1600 rub./5 l.
TELAKKA HEAT
pros
- operates at relatively low temperatures;
- contains anti-corrosion components;
- safe for rubber seals;
- without smell;
- does not contain mercury, chlorine, heavy metals and other harmful components;
- When combined with waste water, it does not form toxic or explosive compounds.
Minuses
- not suitable for products made of aluminum, non-ferrous metals and stainless steel;
- quite high cost.
Telakka HEAT heating system cleaner
SYNTILOR Watesup
This professional product is suitable for washing pipes made of plastic, metal alloys, and rubber. Requires prior testing when used in stainless steel equipment. Requires dilution in 5–15 liters of water. The solution does not destroy seals.
Price: from 450 rub./l.
SYNTILOR Watesup
pros
- operates at low temperatures 20...35 °C;
- does not destroy rubber, plastic;
- does not affect the structure of metals;
- provide protection of metals from oxidation;
- has no pungent odor;
- without mercury, heavy metals, chlorine.
Minuses
- not suitable for cleaning aluminum and aluminum-based alloys;
- relatively high cost.
SYNTILOR Watesup
SYNTILOR Watesup All
The product is intended for flushing heating systems made of aluminum. The product does not destroy seals. Before use, it is recommended to dilute in 5–15 parts of water.
Price: from 480 rub./l.
SYNTILOR Watesup All
pros
- the preparation can also be used for different types of steels, including stainless steel (after a preliminary test);
- the solution is compatible with plastic and rubber pipes;
- does not contain mercury, heavy metals, or other harmful impurities;
- without smell;
- effective at temperatures 20...35 °C.
Minuses
not noticed.
SYNTILOR Watesup All
Fire test reports
During testing for the performance and safe operation of fire equipment, several reports are drawn up:
- checking fire hydrants;
- diagnostics of internal water supply;
- checking for the safety of use and compliance with labor protection rules of fire escapes.
Fire hydrants
Testing the performance of hydrants for water loss is carried out twice a year and is often combined with checking the fire-fighting water supply system. Based on the results of the inspection, an act is drawn up and signed by the commission. Mandatory members: a representative of the fire inspection and a representative from the organization in which the inspection is taking place. Also, the commission may consist entirely of company employees.
The act states:
- general organizational information (information about the company, date and place of compilation);
- the main part describes the members of the commission and the progress of the test. Information about hydrants is presented in tabular form. The location address, diameter, pressure, water yield and affiliation of the hydrant are indicated;
- in the final part, compliance (or non-compliance) with the requirements of the hydrant condition is established.
At the end, the act is signed by authorized members of the commission.
Internal fire water supply
The act establishes the presence or absence of defects and malfunctions in the fire water supply system. The inspection is carried out by responsible employees of the enterprise. Frequency – at least twice a year; for flammable industries, inspections may be scheduled more often.
Internal fire water supply (IFP) is a complex system of pipes, sensors, and switches. Therefore, it is often checked by a labor protection or fire safety specialist, as well as by persons who are trained in fire safety.
The act is drawn up on letterhead or plain paper indicating the details. Be sure to register:
- information about the organization and participants of the inspection;
- information about the object being checked;
- inspection results;
- recommendations for eliminating defects and malfunctions, if any are found;
- signatures of responsible persons.
If additional documents are attached to the act, their list and name are indicated.
Fire escapes
Testing of firefighting equipment, including ladders and stepladders, is regulated by a special GOST. Inspections can be carried out by organizations that have received permission from the Ministry of Emergency Situations and have special equipment for this.
The test results are recorded in the test report. The documentation provides standard information about the organization and its details, information about the members of the commission. The main part provides information about the inspected objects (number of ladders and stepladders, their inventory numbers and affiliation with the structural unit), information about the results of inspections (absence or presence of defects). An instruction is given to eliminate the identified faults.
At the end, the act is signed by the members of the commission.
Flushing heating pipes
Cleaning of the pipeline is recommended before testing. The process is needed to eliminate deposits inside tunnels and radiators in order to prevent inaccuracies in the results of crimping.
Why do flushing before crimping? This procedure will help identify sections of the pipe with thin walls. If a layer of slag has grown on the inside of the tunnel, the line will withstand the pressure testing, but will burst at any moment during the heating season. To prevent such an outcome, it is recommended to first flush the pipes, then perform pressure testing.
Flushing should be done with an electric or manual compressor, with or without dismantling the radiators. The recommended frequency of the procedure is once every 4-6 years.
Methods for cleaning the heating network
To eliminate blockages and accumulations inside tunnels and heating devices, various means and equipment are used.
Let's look at some of them:
- Hydrochemical washing. The process uses special chemicals to dissolve salt and lime deposits. The procedure is not the main one, it is auxiliary, since it does not remove bottom accumulations of silt.
- Pneumatic shock. Removes all deposits inside the tunnels. After exposure to the wave shock, the network is washed with water pressure.
- Sparging or pneumohydraulic cleaning. It is organized by simultaneous supply of air and water under pressure. Efficiency reaches 89%, so bubbling is used most often to remove blockages.
Experts recommend a comprehensive flush that includes all of the options listed. The process is relevant for significantly contaminated pipes or lines with a small cross-section.
Technology
We planned to cover not only the documentation, but also the washing technology. As already mentioned, there are two main methods for performing this work.
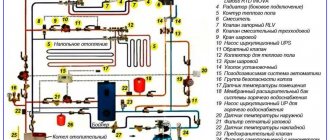
Hydropneumatic technology
This is a common flushing method in multi-occupancy buildings. If a compressor is running near the open door to the basement, and a characteristic gurgling sound is heard in the radiators, your house is being washed with water-air pulp.
The low cost and relative simplicity of the method brought it well-deserved popularity. Alas, pulp is excellent at removing silt, sand and dirt, but it is powerless against rust and lime deposits. In addition, hydropneumatic flushing is associated with the discharge of a large amount of coolant into the sewer system.
How to flush the heating of an apartment building with a compressor yourself?
- One of the house (heating) valves in the elevator unit - supply or return - is closed.
- The discharge into the sewer located in front of it is revealed.
- An air compressor is connected to the control valve near the open house valve. Once it reaches operating pressure (at least 6 kgf/cm2), the valve opens and air space begins to flow into the heating circuit.
- Once the clear water-air mixture has passed into the discharge, the direction of the coolant flow changes to the opposite.
- Upon completion of the compressor shutdown, the water is discharged until air space stops flowing through the discharge in the elevator unit.
A nuance: flushing will be more effective if you close a large part of the risers one by one, so that the pulp flows only through one or two risers at a time. The price of better flushing quality is a greater likelihood of valves coming off on old screw valves when the system is operating from the return pipeline: at the same time, water will move through the valves in a direction that is not normal for them.
Chemical washing
The essence of the method is long-term circulation through the circuit of an alkaline or acidic solution with the addition of corrosion inhibitors. At the same time, rust and lime deposits are completely removed.
It is useful to know about a couple of troubles associated with this method.
| Trouble | Description |
| Reagent disposal | Reagents must be disposed of, usually with their preliminary neutralization. Disposing of acids and alkalis down the drain is prohibited. |
| Selective efficiency | Reagents do not clear sludge from the system. Chemical flushing should be done at the end of the hydropneumatic |
| Possibility of leaks | In a very worn system, alkali or acid will quite possibly cause numerous leaks |
Hydropneumatic flushing
This flushing technique has been used by the domestic housing office for more than a decade, therefore, it is quite effective. Of course, if everything is done correctly.
Video guide
Video air gun Typhoon
Carrying out this procedure is quite simple: water is discharged from the system first on the return line, then vice versa. In this case, the water flow must be “adjusted” with a powerful pneumatic pump. Strong pressure will remove deposits and scale and carry them out of the system.
Regarding the mentioned housing office, the flushing of the heating system, which is carried out by its employees, looks something like this:
- the return valve is closed;
- a pneumatic pump is connected to the valve, which is located after the valve;
- the “return” is reset;
- after the pressure in the pump exceeds 6 kilograms per square centimeter, the valve to which it was previously connected opens;
- all risers are blocked in turn, but so that no more than ten are blocked at the same time; Only if all these conditions are met will the washing be carried out extremely effectively.
The time that the procedure will take can be easily determined by eye, taking into account the degree of contamination of the heating system. New risers begin to be cleaned only after the water from the previous ones comes out completely purified
After flushing all the risers, the system is switched to discharge in the opposite direction.
- the discharge closes, as does the valve to which the air pump was connected;
- the open valve is also closed, after which a similar one on the “return” is opened;
- the system is reset - the device is connected to the valve in the reverse direction, the valve opens, and the device turns on.
The next steps of the procedure are the same as in the previous version, only the water will move in the other direction.
Step-by-step instructions for an independent procedure for cleaning the coolant
It is possible to clean the artificial heating system of a building without a third party. To do this, you will need a pneumatic diaphragm pump capable of raising pressure above 6 atmospheres. Before starting the operation, you need to turn off all the valves and unscrew the radiator end caps with a wrench.
Algorithm:
- Close the resource drain valve.
- Connect the diaphragm pump to the valve located after the shut-off valve.
- Dispose of waste coolant.
- Turn on the membrane pump, raise the pressure to 6 at.
- Open the system valve.
- Turn off all house heating risers one by one. No more than 10 residential highways should be closed per run.
After the operation, you need to connect the pump through the return line to the carrier inlet into the building. However, before this it is necessary to drain the heating. After high-quality treatment of the circuit, the water should come out clear.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
You can see how to flush a heating system that consists entirely of heated floors in this video. The chemical washing method was not chosen by chance, because other options are almost impossible to implement with so many tubes, connections and bends:
Cleaning a separate radiator using the hydropneumatic method is shown and described here:
When choosing a flushing method for your heating system, try to find a balance of convenience, cost and safety for both the pipes and the environment. Remember that it is up to you to live with this system and repair it in the coming years.
How often do you flush your heating system? Do you use the services of professionals or do it yourself? Which washing method do you prefer? Join the discussion on the topic in the block below the article.