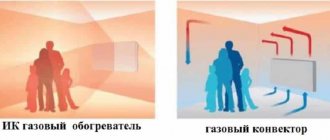
Interest around heating rooms with infrared devices does not subside: some consider them ineffective, others consider them the most comfortable and economical.
Before choosing an infrared heater, you need to understand its technical characteristics and installation nuances, as well as get acquainted with the modern models on the market. It is these issues that our article is devoted to - here we will take a detailed look at the advantages of this type of heaters and highlight the main varieties present on the market.
We will also consider the best models from well-known manufacturers, which users rated higher than others. In addition, the article is equipped with thematic photos and videos with recommendations for choosing the best heater for your home and apartment.
Features of different types of infrared heaters
The result of an IR heater is similar to the effect of the Sun. Radiant heat immediately warms a person, bypassing the air, which increases the efficiency of the device. Walls and objects gradually heat up, which also begin to reflect heat. According to the type of energy carrier, all infrared heaters are divided into electric, gas and liquid fuel. Electric and gas infrared heaters are used to heat domestic premises. At the same time, gas ones are used much less often.
Electric IR heaters
Electric infrared heaters can be divided into light and dark. Light or short-wave IR heaters have glass tubes with spirals enclosed inside as a heating element. They are capable of heating up to temperatures of more than 600 C and emit quite bright light. These devices produce very intense heating in the direction where their heating elements are facing.
Dark or long-wave IR heaters have an operating temperature of less than 600 C and are available in the form of heat-generating panels and films. Most often, such heaters have an operating temperature of 300 C to 400 C. This allows such devices to be hung on a wall or ceiling. IR heaters of this type are not capable of overheating the human body; they can be turned on for a long time.
The operating principle of an electric infrared heater is to apply voltage to the heating element, where, thanks to the internal design, thermal energy is converted into electromagnetic waves emitted in the infrared range, and a metal reflector facilitates their propagation throughout the room. In the case of thin plates (wall-mounted models), the heat spreads over short distances.
A person senses IR rays in the range from 5.6 to 100 microns, based on which heaters with short (2-4 m), medium (3-6 m) and long-range (6-12 m) action are produced. Depending on this, heaters are used both in ordinary houses and apartments, and in production for heating workshops and hangars.
Electric IR heaters are produced in vertical and horizontal housings. According to the type of installation, they are floor-low, floor-mounted with a high stand, wall-mounted and ceiling-mounted. The equipment is effective both indoors and outdoors.
Gas IR heaters
The principle of operation of a gas infrared heater is ultimately similar to an electric one - it also produces radiant heat in the infrared range. But a ceramic plate is used to create it. It is heated by a supply of natural gas and air, which combine in a mixing chamber where flameless combustion occurs. As a result, the main heat is transferred to the porous ceramic plate. The heated ceramics begin to emit infrared rays into the room.
This type of equipment is more mobile because it is powered by a cylinder. The latter is installed nearby or can be moved away from the device thanks to a long hose. The design of some heaters allows you to hide the cylinder inside the housing.
By shape and type, gas IR heaters are:
- household (house, dacha);
- hiking (for tents);
- on a high stand (for street cafes, observation platforms).
Now, understanding the operating principle of the main types of this equipment, let's look at the advantages and disadvantages of infrared heaters relative to oil or convection heaters. This will help you make the right choice for heating your apartment, house, open area or workplace.
Minus number 1. Baking
The heat from infrared heaters is similar to the heat from a stove, fire, or sun (but without the ultraviolet). The intense intensity of this heat feels pleasant at first, but can cause discomfort after a while. To avoid this, do not install powerful heaters on low shelves.
Pay attention to the “Minimum installation height” characteristic of ceiling infrared heaters to avoid the effect when it seems that your head is about to “boil” and your feet are cold
Advantages and disadvantages
Like any other, infrared heating system has advantages and disadvantages. Its positive aspects include the following:
- the room can be heated to 50°C;
- when operating IR heating panels, normal humidity and optimal temperature conditions are ensured;
- during operation of infrared devices, no convection air currents are formed, therefore there is no dust in the house;
- the presence of a thermostat allows you to maintain a certain temperature indoors and save energy;
- infrared heating panels can be placed both on the ceiling surface and on the walls;
- IR devices minimize the temperature difference at the ceiling and at floor level;
- due to the slight inertia of the infrared system, heating of the room begins immediately after it is turned on;
- long service life - 50 years;
- environmental Safety.
Voltage drops in the network are not critical for infrared panels, therefore they are considered quite reliable Source s.06153.com.ua
Types of models
Today you can buy various types of infrared heaters in stores. Let's look at them in more detail, pointing out the main features.
Energy saving ceiling
Such models are placed using fastening elements that are mounted to the ceiling at a height of 2.4 to 3.5 m. These indicators can be changed using adjustable cables. Such a heater must be installed at a distance of at least 3 or 5 cm from the ceiling.
Photo 3. Ceiling infrared heater in a private wooden house. The device is located at some distance from the ceiling.
Their peculiarity is that ceiling devices are most often placed in garages, offices, open summer areas, cafes, and cottages. In some cases they can be used to increase the temperature in greenhouses.
Wall mounted
Serve as an independent source of heating in rooms of various sizes. Wall-mounted appliances must be equipped with a thermostat, which can not only regulate the heating temperature, but also set the time for turning the appliance on and off.
Hang the devices to be analyzed at a distance of at least 5 cm under the windows or above the door. Depending on the cost, heaters can have beautiful paintings, decorative stone trim, and tiles.
Attention! Experts advise purchasing ordinary heaters that are not additionally painted, since low-quality paint during the heating process can release substances harmful to the body.
Floor-standing
Most of these models are portable. Given the significant weight of the device, it is necessarily additionally equipped with wheels, which facilitates the process of transporting it.
Photo 4. Several floor-mounted infrared heater lamps. The products serve not only for heating, but also for interior decoration.
Their peculiarity is that floor infrared heaters are used exclusively as an additional source of heat. Installation in an apartment next to a sofa, armchair, or socket is prohibited.
Important! During use, monitor the cord for overheating. Otherwise, it may cause the wiring to melt and cause a short circuit.
Recommendations for choosing a heating device
Before purchasing, you have to decide: which model of infrared heater is better to choose for your own use? If you are interested in the option of an infrared carbon device, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the varieties and tips for choosing a carbon model.
It is also necessary to determine where exactly the device will be installed, whether it is necessary to transfer it to another room, what heating area should be calculated, which power source is preferable for it.
Power is calculated in the standard way: 1 kW per 10 m², that is, to heat one room you will need a device no more powerful than 2 kW.
Image gallery
Photo from
Heaters for outdoor or terrace
Appliances for the kitchen or nursery
Mobile heating devices
IR equipment for garage
One of the indicators of the “longevity” of home heaters is durable materials and good build quality. Sometimes you can even judge by eye how reliable and functional a thing is.
If there are no nicks, chips or scratches on the body, all parts fit exactly to size, the grille is not deformed, adjustment is free - the product is of decent quality.
If unusual design comes first, the main focus is on wall-mounted electric models. Some of them are made so skillfully that they are difficult to distinguish from paintings or graphic works
Be careful with the cheapest models. Even if you are satisfied with the appearance, you need to look for a catch - perhaps it’s due to low-quality materials or the lack of any protection. Heater safety is one of the main criteria, for which you can overpay.
If the price is higher than usual, then the device is equipped with additional devices that may be useful. For example, a thermostat that controls the temperature, an overheat sensor or a remote control.
Infrared radiation sources
Generally speaking, any body heated to a certain temperature emits thermal energy in the infrared range of the electromagnetic wave spectrum and can transfer this energy through radiant heat exchange to other bodies. Energy transfer occurs from a body with a higher temperature to a body with a lower temperature, while different bodies have different emissive and absorptive abilities, which depend on the nature of the two bodies, the state of their surface, etc.
Electromagnetic radiation has a quantum-photonic character. When interacting with matter, a photon is absorbed by the atoms of the substance, transferring its energy to them. At the same time, the energy of thermal vibrations of atoms in the molecules of the substance increases, i.e. radiation energy turns into heat.
The essence of radiant heating is that the burner, being a source of radiation, generates, forms in space and directs thermal radiation into the heating zone. It falls on enclosing structures (floors, walls), technological equipment, people in the irradiation zone, is absorbed by them and heats them up. The radiation flux, absorbed by surfaces, clothing and human skin, creates thermal comfort without increasing the ambient temperature. The air in heated rooms, while remaining almost transparent to infrared radiation, is heated due to “secondary heat”, i.e. convection from structures and objects heated by radiation.
Popular myths about emitters
Despite the many obvious advantages, the question of the harm of IR heaters stops many from purchasing. Let's try to debunk the most common prejudices regarding radiant heating equipment.
Myth No. 1. IR heaters are dangerous a priori
It is impossible to speak categorically about the dangers of infrared equipment. This is equivalent to saying that the Sun is 100% evil. After all, their action is similar.
On a hot summer day in the sun, especially without a hat, you can easily suffer from heatstroke. But if you choose the right time for a walk, wear a scarf and sit in the shade, the sun's rays will bring exceptional benefits.
The same applies to infrared emitters. Sitting in an embrace with a device of dubious quality is definitely dangerous. But a well-chosen and positioned device from a trusted brand will not do any harm: on the contrary, it will improve your well-being, have a tonic effect on the body and save money on heating.
The effectiveness and safety of infrared radiation in a reasonable dosage has been proven by many scientific studies. A strong argument in favor of IR radiation is its widespread use in medicine and manufacturing (including food production).
Correctly dosed infrared radiation has anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antispasmodic, stimulating and circulatory effects. It should not be perceived as an absolute health threat.
Myth No. 2. Devices burn oxygen
Not a single heater burns oxygen - this is an ordinary story. Oxygen is an oxidizing agent, and combustion is, in fact, a special case of oxidation, accompanied by the release of heat. Oxidize the oxidizing agent? This is some kind of anti-scientific nonsense.
It is more correct to say that heating equipment can “dry” the air (and with it all the mucous membranes) in the room. After all, a decrease in the relative humidity of the air is a natural process when it is heated. Only house dust can “burn” the heater.
By the way, you should not believe the advertising slogans of manufacturers that there are good heaters that do not dry the air at all (read - their products), and there are bad ones (that is, from all other companies). All heating units reduce indoor humidity. ICO is no worse or better than others in this matter.
How to deal with drought? To make it easier to breathe in the house during the heating period, the rooms need to be regularly ventilated, wet cleaning done daily, and perhaps purchase an air humidifier.
High temperature IR devices cannot be used in fire hazardous areas. To avoid burns, do not touch the surface of the operating device.
Infrared radiation ranges
Objects typically emit infrared radiation across the entire spectrum of wavelengths, but sometimes only a limited region of the spectrum is of interest because sensors typically only collect radiation within a certain bandwidth. Thus, the infrared range is often subdivided into smaller bands.
Conventional division scheme
Most often, division into smaller ranges is done as follows:
| Abbreviation | Wavelength | Photon energy | Characteristic |
| Near-infrared, NIR | 0.75—1.4 µm | 0.9-1.7 eV | Near-IR, limited on one side by visible light, on the other by water transparency, which deteriorates significantly at 1.45 µm. Widespread infrared LEDs and lasers for fiber and airborne optical communication systems operate in this range. Video cameras and night vision devices based on image intensifier tubes are also sensitive in this range. |
| Short-wavelength infrared, SWIR | 1.4-3 µm | 0.4-0.9 eV | The absorption of electromagnetic radiation by water increases significantly at 1450 nm. The range 1530-1560 nm predominates in the long-distance communication region. |
| Mid-wavelength infrared, MWIR | 3-8 µm | 150-400 meV | In this range, bodies heated to several hundred degrees Celsius begin to emit. In this range, thermal homing heads of air defense systems and technical thermal imagers are sensitive. |
| Long-wavelength infrared, LWIR | 8—15 µm | 80-150 meV | In this range, bodies with temperatures around zero degrees Celsius begin to radiate. Thermal imagers for night vision devices are sensitive in this range. |
| Far-infrared, FIR | 15—1000 microns | 1.2—80 meV |
CIE scheme
The International Commission on Illumination recommends dividing infrared radiation into the following three groups:
- IR-A: 700 nm - 1400 nm (0.7 µm - 1.4 µm)
- IR-B: 1400 nm - 3000 nm (1.4 µm - 3 µm)
- IR-C: 3000 nm - 1 mm (3 µm - 1000 µm)
ISO 20473 diagram
The International Organization for Standardization proposes the following scheme:
| Designation | Abbreviation | Wavelength |
| Near infrared | NIR | 0.78-3 µm |
| Mid-infrared | MIR | 3—50 µm |
| Far infrared | FIR | 50—1000 µm |
Astronomical diagram
Astronomers usually divide the infrared spectrum as follows:
| Designation | Abbreviation | Wavelength |
| Near infrared | NIR | (0.7…1) – 5 µm |
| Mid-infrared | MIR | 5 - (25...40) µm |
| Far infrared | FIR | (25...40) - (200...350) µm |
Why is it harmful to the body?
Some experts claim that radiation has a negative effect on the human body; they claim that the waves cause diseases of the eyes, skin, as well as the nervous system and blood. Other experts say that infrared heat is good for health: it has a positive effect on metabolism, skin and muscles. However, there are independent studies that show that the waves emitted by emitters are harmful.
In case of prolonged exposure to infrared, the eyes become more susceptible to harmful radiation, and headaches may begin. In extreme cases, with extremely prolonged exposure, cataracts can occur as a result of the initiation of chemical processes in the white of the eye. It is worth noting that infrared radiation with short waves, quickly penetrating through tissue, reaches the structures of the eye faster.
Far infrared light is used to heat rooms in which people are located. This is radiation that is easily absorbed by particles of liquid that are present in the human body. Therefore, cells (especially skin) are heated in a certain sense directly and quite quickly. But the power emitted by the heater is small. This range is considered completely safe, as confirmed by studies presented by the manufacturers.
According to scientific research, only long-wave infrared devices have a positive effect on the human body. But this process should be short-term. Otherwise (with prolonged directed heating), according to professionals, the skin will be overheated and dry out, which will have a bad effect on its condition. In addition, it is possible to burn the retina and lens of the eye, so experts do not recommend looking at the heater coil for a long time.
Making your own infrared heater
Below we will briefly describe how to make a simple infrared heater with your own hands from scrap materials that are almost always present in the household. For a person, as they say, with hands, this will not be difficult. To complete the work, you will need the following materials and components: aluminum or copper foil, two glass rectangles of the same size, an ordinary candle, any sealant, epoxy quick-hardening glue, a powerful electrical power cord with a plug, a napkin, cotton swabs and a multimeter.
Below are step-by-step instructions for making your own small IR heater.
- We clean the glass from dirt with a napkin and apply a layer of soot to one side of each, using a candle. It is necessary to ensure that the soot lies evenly without gaps. Using a cotton swab, clean the edges of the glass from soot by 5 mm along the contour.
- Using a multimeter, you need to measure the resistance of the soot layer on each glass. It should be approximately 48 ohms. If this indicator is less, remove some of the soot with a cotton swab, and if it is more, apply another layer of soot with a candle.
- Assemble the structure. To do this, place pieces of foil that will become electrodes on the soot layer of one glass, apply epoxy to the surface of the glass, and cover the structure on top with another glass with the soot layer down.
- After the glue has dried, coat the ends of the structure with sealant. The heater is now ready for use. The resistance of the conductive layer will be 24 Ohms, which, when connected to a 220 V network, will provide a power of 2 kW.
- The manufactured structure should be placed on a wooden block with metal plates, to which a power cord with a plug must be connected. The foil petals should be pressed tightly against the metal plates.
Important! The pictures show an experimental low-power heater. To make a more powerful infrared heater, you should use glass of a different size, approximately 50x50 cm
This completes the making of an infrared heater with your own hands. Of course, you can place an additional sheet of foil under the entire structure for greater heat transfer, but this is at your discretion. Even without it, such a device is capable of heating a small room!
Minus number 4. Dependence of efficiency on floor material
Most of the heat from ceiling-mounted infrared heaters reaches the floor. The floor heats up 1-2 degrees more than the ambient temperature and begins to give off heat to the air. For the floor to heat up, it must be well insulated and have low thermal conductivity. Floors made of wood, linoleum or laminate have these properties. If the floor is made of tiles or porcelain stoneware, but with a layer of insulation, then the efficiency will be lower and it will take longer to warm up. The worst option is a concrete or tile floor laid directly on the ground without insulation. This often happens in basements, garages or cellars. The main part of the heat will be absorbed by such a floor and go into the ground. It is impossible to warm up the entire earth; therefore, the efficiency of heaters in this case will be extremely low or even zero.
For those who need more: two-in-one heaters
An interesting (and expensive) class of hybrid devices are convection-infrared heaters, which combine the advantages of convection and infrared heating. In addition to the infrared heating element, they are equipped with an additional heating element, which heats the air in the usual convective way. Thanks to this combination, both the air and the surfaces in the room warm up - this speeds up the achievement of a comfortable temperature and allows it to be maintained for a long time after the device is turned off. Convective-infrared heaters are often equipped with a micathermic heating element, so their surface does not heat up to dangerous levels. The most expensive devices of this type have a very efficient design with a glass ceramic front panel, a touchscreen display and even Wi-Fi connectivity. In terms of accuracy and flexibility of settings, heaters of this type are practically unrivaled: their temperature adjustment steps can be less than 1 degree. The power of such devices is from 1 to 2.5 kW, and the design is floor-mounted or wall-mounted.
Advantages of convective-infrared heaters:
- quick heating of the room;
- long-term temperature maintenance;
- low surface temperature - no risk of burns;
- ease of control;
- high energy efficiency.
Minuses:
- price;
- dry air (albeit to a much lesser extent than from conventional convectors).
Convective-infrared heater (photo from obi.ru)
Reviews from doctors
Yes, there are health risks from infrared radiation, but this occurs when heaters are not used properly. So when weighing the pros and cons of infrared heat, just remember: “it’s the dosage that separates the medicine from the poison.”
Gunkov I.N.
Even if the device was selected according to the area of the house, this cannot be a guarantee of absolute safety. The device is harmful if used for a long time, especially if it was installed in violation of safety regulations. Even if there are no serious consequences, the eyes and skin may be damaged.
Ivanov N.F.
With frequent and long-term use of such heating devices, negative consequences from exposure to infrared rays may occur. Here you need to take into account the type of device, choose a heating device that emits long waves. But for patients with weakened immune systems, the influence of such a heating device is sometimes even beneficial.
Romanenko I.I.
Safety precautions
Installation and connection of the heater must be carried out only in accordance with safety regulations. If the technical requirements are met, the device will be safe for health even with prolonged use - 24 hours a day.
Forbidden:
- operate the heater without grounding;
- use the device in rooms with the presence of flammable liquids, steam-air mixtures, flammable dust or fibers, in very dusty rooms and during repairs;
- wipe the radiating plates with flammable liquids while the heater is operating;
- install the heater next to furniture and curtains;
- leave the device turned on unattended;
- use a clothes dryer.
You should purchase original devices from trusted manufacturers, made of quality materials.
Methods of protection
To reduce the negative impact of a heater on health, you need to follow a few simple rules.
Helpful Tips:
- Do not place the heater directly above a place where people are constantly present; it is better to install it in the far corner of the room.
- Avoid sleeping near short-wave infrared light as it may cause dry skin.
When choosing a heater, you don’t need to give preference to the cheapest options. The cost of such a device can only be reduced by using low-quality materials that release hazardous elements into the air when heated.
Power
The standard recommendation is to calculate a power of 1000 W per 10 square meters. m. However, here you need to take into account some nuances:
- for apartments with many windows, thin partitions, corner location, it is better to add 20-30%;
- if the IR emitter will be the only source of heat, then it is wise to take a heater with a reserve;
- in the case when such devices are auxiliary, it is necessary to take into account the initial temperature parameters;
- when you need short-term heating of a small area, choose a low-power model with ratings of at least 300 W.
Possibilities
Using the device will become more convenient and safe if it is equipped with the following options.
- Thermostat – set the desired temperature, and the equipment will turn off automatically at the right time. And vice versa: when the room cools down, the device will turn on.
- Tip-over protection is required for floor-standing units to prevent fire. If you accidentally touch the device and it falls over, it will shut down.
- Overheat protection - when a critical temperature is reached, the unit turns off, regardless of your actions. This will protect against fire and damage.
- Remote control is common in ceiling products and allows you to configure equipment even at a distance from it.
Wavelength
Another important characteristic is the emitted wavelength. The temperature that the fireplace can produce and your health depend on this.
For housing, devices with long-wave radiation (about 10 microns), which are completely absorbed by the epidermis, are recommended. They are absolutely safe and do not affect your well-being in any way.
Short waves (2-3 microns) can penetrate body tissues, causing headaches and dizziness. Another negative effect is the appearance of burns. Such devices are used in production workshops with high ceilings.
Useful tips
Which infrared heater do you choose?
CeramicCarbon
When choosing an infrared heater, you should check with the seller for some characteristics:
- The anodizing coating on the emitter must be at least 25 microns thick. This will ensure a long service life of the unit (over 20 years). If the coating is thinner, then there is a risk of rapid failure of the emitter.
- For rooms with high humidity, it is preferable to choose devices with a heater made of stainless steel. In other cases, you can get by with ferrous metal products.
- The foil of the radiating element must be 120 microns thick. At a lower value, the heat will go to the ceiling rather than spread throughout the room. You can check this characteristic yourself. To do this, take a writing pen and press the rod onto the coating. Any damage that occurs indicates poor quality and thin foil. It will not be possible to push through a good coating.
You can purchase a high-quality product that fulfills its purpose well by taking into account the main characteristics of heating units, the purpose and place of their use, the size of the room and the installation features.
Exploitation
- Do not install such equipment in rooms where explosive materials are located.
- When purchasing a floor heater, you just need to place it on the floor, point it in the direction that needs heating, and turn it on.
The ceiling or wall option must first be installed using the mounting system, which is always included.
Installation and connection of the unit must be carried out by qualified specialists.
- If there are voltage surges, you need to additionally purchase a stabilizer.
- It is necessary to periodically wipe the disconnected device with a damp cloth to remove dust.
- Do not touch a heated device.
- Avoid mechanical damage.