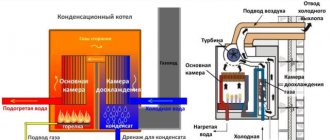
Gas-fired heating boilers are devices characterized by increased hazard properties. If such a device is not used correctly, it can cause problems such as:
- spontaneous combustion resulting in fire;
- people can get carbon monoxide poisoning;
- Gas poisoning may occur due to leakage;
- an explosion may also occur.
To prevent such dangerous situations that may result in human casualties, all processes that take place in heating boilers are placed under automatic control. Automation for gas boilers exercises vigilant control to ensure that all systems work clearly and smoothly.
All installations that provide heat to homes and premises and operate on natural gas are certified only if they have a high safety class, and this is achieved only through the use of automation for gas heating boilers.
Possibility of boiler operation
Despite the variety of automatic modes, as a rule, only one of the possible ones is used: in which the boiler heats up to the value set on the control panel and continues to maintain it. This mode is acceptable, but not optimal. Based on the coolant temperature, the boiler operates in modulation mode, which is good. At the same time, the boiler devices do not have data about the situation at the facility that serves the heating device. No room temperature data available. There is only one parameter: coolant temperature. When the set value is reached, the boiler power is reduced. Then the heating pad turns off and the device remains idle for some time. As soon as the media temperature drops by a set number of degrees, a restart occurs.
+ The boiler operates in modulation mode.
— Gas consumption increases, since only one parameter affects the boiler power.
How to choose a UPS?
When choosing a backup uninterruptible power supply for a gas heater, you must take into account the power consumed by the boiler. The more electricity it consumes in the process of heating the coolant, the more capacious the battery is needed. Otherwise, the battery life will be too short. Power outages sometimes last for several hours. If the capacity of the uninterruptible power supply is only enough for a few tens of minutes, then it will be of zero use.
There are three criteria for choosing a UPS for gas heating equipment:
- Water heating boiler power;
- Battery type;
- Operating time from source.
The selected power depends not only on the boiler itself. If the system has a circulation pump and other energy-dependent devices, without which normal heating operation is impossible, then this must be taken into account. Their consumption must also be added to the boiler parameters. Existing do-it-yourself heating schemes for a private house are very diverse; they often contain a huge amount of “smart automation”. However, all these devices consume electricity.
Car batteries cannot be used to provide uninterrupted power supply to a gas boiler. Technically they can be connected. However, they were initially designed for completely different operating conditions. The designers included in them the need for short-term current output when starting the car engine.
If you equip the UPS in question with them, then car batteries will not last long under constant loads. Most of them are simply afraid of deep discharge. Plus, electrolyte evaporation is unacceptable in residential areas.
For gas boilers, you should take batteries made using AGM or GEL technology. In the first, the electrolyte simply does not evaporate due to the solutions used in manufacturing, and in the second, instead of it, a special gel is poured between the battery plates.
To calculate the UPS capacity in a particular case, you should multiply the hours (how long your lights usually turn off) and the boiler power (according to the data sheet), and then divide them by a factor of 8.65. For example, for autonomous operation for 12 hours of a 24 kW heater with an electrical power consumption of 130 W, one 24 V battery or two 12 V batteries are required. C = (150 * 12) / 8.65 = 180 ampere-hour. Most 12 V batteries are usually rated at 100 Ah, so you will need two of them.
When choosing a device for uninterruptible power supply to the boiler, you should also look at:
- The presence of the mark “pure sinus”;
- Charge current parameters (from 4 to 20 A);
- Switching time to battery (0 to 1 second).
The higher the charge current, the faster the battery will be filled with energy. However, charging too quickly is contraindicated for some batteries. If the boiler is equipped with precise electronics, then the transition time from the mains to the battery should be zero. Delays and interruptions in power supply are unacceptable here.
The main point is “pure sine”. If the UPS data sheet states “approximated sinusoid” or “step approximation of a sinusoid,” then such an uninterruptible power supply is intended for computers and televisions. You cannot power a gas boiler from it.
To power both the electric motors of the circulation pumps and the burners, a precisely sinusoidal voltage is required. With a fuzzy sine wave, parasitic currents arise in the electric motor, causing overheating and burnout of the winding insulation. And such a supply voltage is absolutely contraindicated for the ignition electrodes of the burner.
Connecting the thermostat
When connecting a conventional thermostat to the boiler (as an element of automation), operating comfort increases and gas consumption is reduced. This occurs due to the fact that the boiler is controlled by a sensor installed in the thermostat itself and turns off the burner when the set air temperature is reached in the room.
Taking into account the fact that the volume of air in the room is several times (or even tens of times) greater than the volume of the coolant, its cooling rate is several times lower than the rate of temperature drop in the boiler.
However, in this operating mode it is impossible to adjust the coolant temperature using the thermostat itself. Therefore, the value on the boiler is most often set to the calculated maximum. This is done to ensure that the boiler reaches the set temperature as quickly as possible. However, this method has one negative side. The media temperature either rises to maximum or drops almost to room temperature during idle time. During the off-season, this can lead to uncomfortable sensations. The radiator is either cold or hot - this is not very convenient.
+ Gas consumption is reduced.
— Temperature range of heating equipment from maximum to room temperature.
Design and operating principle
The automation that controls the operation of a gas boiler consists of many elements, conditionally divided into two subgroups. The first includes mechanisms that ensure the full and safe functioning of the boiler itself. The second includes devices that make it possible to operate the heating system in the most convenient and user-friendly mode.
Components of a security system
Several modules are responsible for the operational safety of the unit:
- Flame controller - consists of two main parts - a solenoid valve and a thermocouple. Shuts off gas promptly and reliably and prevents leakage.
- Thermostat - maintains the set temperature of the coolant and protects the system from overheating. When the coolant cools down to minimum temperatures, the module starts the boiler into operation, and after recording peak-high readings, it turns it off, completely relieving the owners of the need to constantly pay attention to the system.
- The draft control sensor is responsible for stopping the gas supply to the burner in the event of a change in the basic position of the bimetallic plate, thus preventing gas leakage.
- Safety valve - monitors the amount of coolant in the circuit.
In addition to all the above useful qualities, the automation has a number of additional functions that increase the comfort of using the equipment.
The device performs automatic ignition of the gas burner, selects the most effective operating mode, promotes rational consumption of energy resources and conducts independent diagnostics, saving the owners from all these activities.
Operating principle of security automation
Current regulatory documentation says that the safety system for gas boilers must be equipped with a device that stops the operation of the entire system and shuts off the gas supply in the event of an unexpected breakdown or any other force majeure circumstances.
To carry out this task, automation must keep under control such parameters as:
- gas pressure in the system;
- presence of an optimal size flame in the burner;
- full, high-quality traction;
- working coolant temperature level.
When the gas pressure in a non-volatile mechanical system drops to a critical level, the resource supply immediately stops. This happens automatically due to the presence of a valve mechanism set to a certain value.
Volatile electronic devices are designed slightly differently. In them, the above function is performed by a minimum/maximum pressure switch.
As the number of atmospheres increases, the membrane with the rod bends, opening the power contacts of the boiler itself. Gas stops flowing and is not supplied until the pressure level is restored.
It is prohibited by law to independently troubleshoot problems and somehow interfere with the basic functionality of the equipment. Only a qualified specialist - an employee of the gas supply company - can correct any problems that arise.
If the flame disappears in the burner, the thermocouple cools down and stops producing current. After this, the electromagnetic damper in the valve no longer functions and gas stops flowing to the burner. When the thrust drops, the bimetallic plate heats up intensely, changes shape and acts on the valve, causing it to stop supplying fuel.
The coolant temperature is kept under control by a thermostat. It ensures that the user-selected heating mode is maintained, while preventing the system from overheating and failing.
Nuances of the system's functioning
Volatile electronic automation operates based on information received from sensors. The microprocessor and internal controller analyze this data, process it and provide the system with commands that are optimally suited for a particular situation.
In order for electronic automation to function normally for a long time, it is necessary to call a technician annually to inspect the equipment, diagnose the microprocessor and view memory module reports
Mechanics have a slightly different principle. When the boiler is turned off, the internal gas valve is completely closed. At the moment the equipment is started, the washer on the valve is squeezed out and the passage for the fuel resource to the igniter is forced to open. Ignition stimulates heating of the thermocouple and voltage is generated across it.
This resource uses an electromagnet to maintain the valve in the open position. By turning the washer manually, the user can effortlessly adjust the level and power of his heating equipment.
Connecting the chronothermostat
A special case of using automation in the form of a normally open contact thermostat is the use of a chronothermostat. On the thermostat itself, time periods are set and two or three heating levels are set: the lowering temperature is “night” and the temperature is “day”. But in any case, the coolant temperature will be the one set from the control panel.
+ The boiler heating differential is set based on the user's needs.
— The temperature set from the control panel is adjusted manually.
Weekly programmer
More advanced device. It has broader functions and capabilities for controlling the indoor climate. You can choose either a preset mode or customize it yourself. The cycle is set for a week and, accordingly, is repeated weekly. The most commonly used connection is via a radio channel.
The devices vary in design and color, so you can choose a programmer to suit your taste and interior, which is also a small but pleasant plus.
Connecting an analogue modulating controller
Another possibility for operating boilers is to use, together with the boiler, not a disconnecting thermostat, but an analogue smooth-action regulator. This allows you to control not only the room temperature, but also adjust the burner power due to feedback. Communication with the gas boiler automation is carried out via a wired or wireless line. It becomes possible to track various parameters that depend on a specific model.
Since this will already be an electronic device, it often immediately becomes possible to control the chronoprofile, that is, heating periods and waiting periods for the boiler are set. You can set several different temperature levels.
General classification of gas burners by fuel type
Country houses cannot always be supplied with natural gas supplied from a public main. Therefore, the burners are varied in terms of using different types of fuel. If the fuel comes from the gas main, propane-butane gas burners are most likely used for heating boilers.
Trunk methane gas is the most affordable natural fuel for boilers. However, now there is no big benefit in the price of liquefied blue fuel (propane-butane mixture). General heating provided by the main pipeline is also expensive.
Gas boilers operating on different types of fuel mixtures have approximately the same design. There is a slight difference in cost, but it is also insignificant (equipment for liquefied fuel will cost more). The burners themselves are slightly different, having different nozzles for liquid fuel and blue gas.
If natural gas is not supplied to the house, propane-butane gas burners are used
Propane burners require adjustment to this type of fuel with the installation of a nozzle. When burning, the flames give off a yellowish color, and more soot accumulates in the chimney. The jet is responsible for normalizing pressure.
Modern burners operate in a wide temperature range – from -50 to +50 °C. Some equipment can be adapted for other types of energy carriers:
- used oil;
- diesel fuel;
- fuel oil;
- kerosene;
- propane butane base;
- Arctic diesel fuel.
Modern devices often include both types of injectors or universal equipment for fuel types, making them easy to reconfigure.
Homemade gas burners are most often used in solid fuel boilers
It is safer to purchase simple gas equipment adapted for bottled gas. Homemade equipment, although more affordable, is unsafe! Usually, “reworks” are carried out on the basis of old units.
Connecting the Openterm protocol controller
The smooth action controller exchanges an analog signal with the control board. Depending on the rate of heating of the air in the room, it makes adjustments to the temperature supply, reduces the burner power, or, on the contrary, increases it if the temperature is too low.
Another additional feature is that when exchanging data with the boiler control system, a blocking indication can be seen on this controller. That is, if the boiler stops, you can see this without going to the boiler itself, but directly on the display of the sensor located in the room.
+ The device automatically adjusts the heater power based on a number of parameters.
— Quite a high price.
The most common breakdowns in the control unit
Since the control unit is a whole system, a failure can occur from any deviation of a component of this system. The most common malfunctions and their causes:
- the burner went out - air got into the gas pipeline;
- heating problems - poor gas supply, lack of oxygen;
- boiler overheating - closed contacts, prolonged operation at high temperatures, factory defective sensors;
- breakdown of the pneumatic relay (draft sensor) - incorrect connection, fan breakdown, incorrect smoke exhaust system;
- breakdown of the temperature sensor - incorrect connection of contacts, short circuit, overheating of the board;
- breakdown of the pressure switch - low water pressure in the pipes, defective contacts in the circuit board.
Most of these problems are easily fixed, even described in the instructions, but some require the intervention of a specialist.
You should not replace sensors or other parts yourself - this can be dangerous.
Connecting weather-compensated automation
Some boiler models are equipped with the ability to use weather-dependent automation that supports the Openterm protocol. Due to the use of an external temperature sensor, additional variables appear that make it possible to more quickly adjust the burner power and supply temperature, depending on the changing conditions outside the building. Such automation is capable of switching to summer mode on its own: turning off the heating, which will be an additional saving on gas consumption.
+ Intelligent control of the heating device, requiring minimal intervention from the owner, saving fuel.
— Quite a high price.
What automatic settings are there?
Currently, the market offers consumers a wide selection of control devices. Therefore, you need to know what automation systems for home heating systems generally exist, and what to give preference to.
Room thermostat
According to installation criteria, there are:
- Wired thermostats. The advantage of this type is the ability to supply power up to approximately 50 meters via wires.
- Wireless thermostats. The advantage is that it is not necessary to create holes for the wires. However, they have a significant drawback - reinforced concrete walls reduce the signal power.
According to functionality they are distinguished:
- Simple thermostats. They retain the desired level of warmth.
- Programmable thermostats. Such devices are capable of setting a certain number of degrees for a whole week in advance (the period depends on the model) with maximum accuracy down to seconds. The advantages also include cost savings due to weekly programming.
Thermostats are also distinguished:
- Electronic thermostats. The kit contains three components: temperature sensor, signal transmitter, relay. The main advantage of the device is the maximum accuracy of the equipment. Don't forget ease of use.
- Mechanical thermostats. The basis of the devices is the ability to change properties under the influence of temperature levels. Due to temperature changes in the gas membrane, a circuit is closed or opened, causing certain mechanisms to work.
- Electromechanical thermostats. The mechanism of the device is much simpler than an electronic one. The main element is the relay. The node looks like a tube, which is filled with a special substance that reacts to temperature. If the boiler heats up, the substance expands; similarly, when the boiler cools, the substance contracts. And the drive, dependent on the substance, regulates the temperature thanks to an electrical circuit.
Connection can be made to:
- Kotlu;
- To the pump;
- Servo drive;
Thermal head
This is a thermostatic element that, under the influence of the external environment, slightly opens or closes the radiator. An inexpensive type of automation for heating a home. A significant advantage is that the thermal head is very convenient for local heating, and there are also significant cost savings. Of the minuses: firstly, the adjustment occurs according to standards consisting of abstract numbers, not degrees. Secondly, the sensor measures the degree of heat around the installation, but not the room, which reduces the accuracy of the device.
Weather-compensated automation
The design of weather-dependent automation for heating a house is simple: as the weather outside decreases, the temperature of the coolant increases. However, a weather-dependent installation has a very significant drawback - the system sometimes does not have time to adapt to the temperature, and, therefore, the effect is delayed. The especially mentioned disadvantage manifests itself if an addition is connected - heated floors. The disadvantages include the fact that the devices do not operate entirely correctly, approximately, so the change is noticeable only during seasonal climate changes. It is worth noting that the prices for the unit are relatively high. But the units will be very convenient in production, large-scale houses (over 500 square meters).
Automation from different manufacturers
Wall-mounted gas boiler
If we talk about a standard wall-mounted gas boiler, then it can operate according to the coolant temperature. A room thermostat or chronothermostat can be connected to it. It is also possible to connect an openterm protocol regulator.
A special case of using wall-mounted boilers is the possibility of using weather-dependent automation. Due to the use of an external temperature sensor, additional variables appear that make it possible to more quickly adjust the burner power and supply temperature, depending on the changing conditions outside the building.
Automation Arbat
The devices have 5 degrees of protection. There is thermoelectric flame protection. The gas supply is blocked when switched off. A modulating thermostat will provide comfort in use, and a coarse mesh filter will extend its service life.
Some models are equipped with a circulation pump. The device distributes the coolant evenly throughout the heating system. It is also possible to connect to an external thermostat inside or outside the room.
Automation Honeywell
Honeywell has a wide range of automation systems for gas boilers, from the most budget (mechanical) to multifunctional automatic systems.
Main features:
- the coolant automatically maintains the temperature;
- turning off the boiler in case of gas supply interruptions;
- shutdown in the absence of draft or during reverse draft;
- blocking the gas supply when the gas burner goes out.
Some models are equipped with programmable automation with the ability to set temperature periods depending on the time of day, weather, and even develop a heating/cooling mode by day of the week. And the Smile series models control several temperature circuits at once (heating, ventilation, “warm floor”, hot water, etc.).
Mechanical
Mechanical automation for gas boilers does not require connection to the electrical network. This is the main advantage. However, it is not always completely mechanical. It can use a built-in power source - a battery or an accumulator - and use other sources, such as a thermocouple, which produces an emf when exposed to high temperatures. Energy independence still remains, which is ultimately what is required. All settings are set manually, and with a significant error.
At the moment, one automatic control system has become widespread - EuroSit 630. This automation unit with Italian roots turned out to be so good and practical that it is installed on almost all gas boilers with non-volatile control. It is produced in many countries with or without a license.
Automation unit EuroSit 630
The mechanical automation unit is a metal case with a labyrinth inside through which gas can pass from inlet to outlet. A number of valves regulate gas supply, pressure and flow depending on operating conditions and settings. Two control knobs set the boiler operating mode and the target coolant temperature setting.
The main handle defines three operating modes:
- complete shutdown;
- lighting the fuse;
- main combustion mode.
In the first mode, the gas supply is completely stopped.
In the second mode, only the igniter operates. This is a small burner with minimal gas consumption, which burns constantly and is needed to ignite the gas in the main burners of the combustion chamber. By pressing the switch handle, the damper on the gas path to the igniter opens. The igniter is ignited using the piezo ignition button. A temperature sensor or thermocouple is attached next to it. Under the influence of high temperature, an EMF of approximately 25 mV is generated on the sensor, which is enough to power an electromagnetic relay that keeps the damper constantly open. When the thermocouple warms up well, release the handle and the igniter will not go out. If for some reason it goes out, the thermocouple will cool down and the relay will close the valve again.
In the main combustion mode, the automation opens the flow for the bulk of the gas on its way to the burners. The gas ignites from the igniter, the heat rises to the heat exchanger and is transferred to the coolant.
The valve responsible for the gas supply is connected to a temperature sensor, which is attached to the outlet of the heat exchanger. A sensor is a vessel filled with a liquid or gas that can expand or contract greatly when the temperature changes. The vessel is connected via a thin copper tube to the automation unit and exerts pressure on the valve stem.
The adjustment knob sets the valve response thresholds depending on the pressure exerted by the sensor. If the coolant temperature is lower than that set by the regulator, then gas supply is allowed. When the maximum permissible temperature is reached, the gas supply stops.
Another temperature sensor is installed before exiting the chimney. It reacts to the temperature of the exhaust gases. If they are too cold, it means there is no draft, or the burner is not working, there is no fire. In any case, this is a signal to shut off the gas. If the temperature of the exhaust gases is too high, it means that combustion is maintained too intensely, which should also be stopped.
A number of adjustment bolts, not accessible to the user during normal operation, allow you to:
- set the permissible gas flow and pressure;
- set the minimum gas pressure;
- adjust the limits of temperature change of the coolant.
Their installation should be carried out by a specialist during installation and initial setup of the gas boiler.
A common problem with non-volatile automation is the incorrect operation of temperature-sensitive elements. The thermocouple on the igniter is difficult to produce, and the output characteristics of each sensor vary greatly even within the same batch, which gives a significant error in the operation of gas boilers. The situation is simplified by the fact that even a non-specialist can replace a thermostat or thermocouple; they are commercially available and are often interchangeable.
Steam boiler diagram
Coolant flow diagram
PCs are installed in the boiler room, which can be located in separate, adjacent and built-in non-residential buildings.
Designations according to the diagram:
- Gas steam boiler fuel supply system, No.1.
- Combustion device - firebox, No2.
- Circulation pipes, No.3.
- Zone of steam-water mixture, evaporation mirror, No.4.
- Direction of feed water movement, NoNo5,6 and 7.
- Partitions, No8.
- Gas flue, No.9.
- Chimney, No.10.
- Output of circulating water from the steam boiler tank, No.11.
- Purge water drain, No.12.
- Boiler top-up with water, No.13.
- Steam manifold, No14.
- Steam separation in the drum, NoNo15,16.
- Water indicator glasses, No17.
- Saturated steam zone, No.18.
- Steam-water mixture zone, No.19.
Application of the SABC system
SABC automation is a pneumatic, direct-acting manometric system. It does not require an additional power source, so it can be used in non-volatile heating systems.
The SABC system is used to control gas and combined water heating boilers.
Read a review of domestic gas heating boilers from leading manufacturers here.
You will find information about the design and operating principle of pellet heating boilers at the link -
Also read about choosing a heating boiler for a sauna.