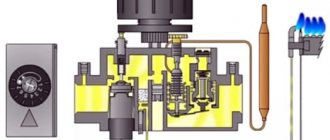
The stability of operation and durability of the heat exchanger directly depend on regular maintenance and cleaning of elastic gaskets, plates, and other components and parts from contamination. For this purpose, special means are used for washing heat exchangers. Let's look at what they are below.
Figure 1 - Flushing agent
Types of pollution
The coolant liquid contains various dissolved elements, which disintegrate when heated, forming an insoluble precipitate - scale. In most cases, pollution forms:
- organic and fatty sediments;
- calcium carbonate;
- iron oxide;
- salt;
- limestone.
Plaque gradually builds up on the inner walls of the heating equipment. If you do not clean regularly, the thickness of the sediment increases. This impedes the circulation of the working medium, reduces the efficiency of the device and prevents its normal operation.
Cleaning Frequency
There are no strict requirements for rules on the frequency of flushing heat exchangers - there are only recommendations indicated in the Operation Manual attached to each device. Recommendations should be adjusted in accordance with the specifics of use - the chemical properties of heat-carrying media, their physical contamination, etc. In particular, it is indicated to carry out cleaning when contaminating deposits of any nature with a thickness of more than 0.3 mm are detected during a routine inspection on heat exchange surfaces.
In practice, the presence of such deposits may be indicated by an excessive decrease in the thermal characteristics of the device recorded by external measuring instruments. Some manufacturers produce modern heat exchangers with a certain “margin”, i.e., taking into account the thermal resistance of contaminants. For them, the presence of deposits exceeding 0.3 mm is allowed - if the heat transfer parameters are within normal limits.
Washing methods
Gasketed plate heat exchangers are washed using chemical and mechanical methods. The first option, as a rule, does not require disassembling the equipment, which is why it is the most popular. Mechanical cleaning is necessary when heavy contamination is detected. The technique involves dismantling the system and involves significant labor costs.
Figure 2 — Flushing the heat exchanger
Where is it located and how to remove it
Basic methods involve completely removing the heat exchanger from the boiler. Cleaning without disassembly and removal is possible only when using the hydrodynamic flushing method, carried out exclusively by specialists. However, the extraction process does not require special skills or special equipment, and the design of all models of gas boilers is not fundamentally different.
The location of the heat exchanger using the example of a wall-mounted Baxi LUNA-3 Comfort 240 Fi.
- The first step is always to remove the front cover; simply unscrew the bolts and carefully remove it.
- We drain the water from the boiler through the appropriate outlet valve (usually located inside the boiler), be sure to release the pressure if there is any.
- Next, you need to remove the front combustion chamber cover. In simple models it is immediately visible; in more complex models, the combustion chamber can be insulated with fire-resistant, heat- or sound-insulating material, or rubber seals. It may also be necessary to remove the top of the combustion chamber.
- Typically, temperature or water flow sensors are installed on the pipes of the heat exchanger, which must be turned off.
- All that remains is to remove the fastening mechanisms, clamps, disconnect the pipes and remove the heat exchanger. Be careful, as when disconnecting the heat exchanger, residual water may flow out of the heat exchanger; cover the electronic components and wiring under the combustion chamber.
In floor-standing gas boilers with an open combustion chamber, the process is even simpler, since the heat exchanger is accessible immediately after removing the housing cover. In general, you can study the structure of your boiler model using the images of the operating instructions; for many models there are visual examples of disassembly analysis on YouTube.
Selecting a cleaning chemical
When choosing a chemical reagent for cleaning a heat exchanger, the main rule is:
The components of the chemical reagent must be aggressive towards scale, but neutral towards the exchanger plates, elastic elements and other parts of the system. This is the only way to effectively remove contamination without harming the mechanisms of the unit.
Criteria for choosing a means for flushing heat exchangers:
- thickness and amount of plaque on the walls inside the equipment;
- material for the production of sealing gaskets and plates;
- chemical composition of pollution.
To reduce the risk of damage to the internal parts of the system, it is recommended to analyze the resulting sediment and, based on the data obtained, choose the most effective but safe remedy.
Current and major repairs of heat exchangers
Routine repair of a heat exchanger is the prompt elimination of defects in heat exchange equipment. The need for such an event as heat exchanger repair may arise in situations such as:
- leakage in one or more places between the plates;
- flow of media from circuit to circuit.
Overhaul of a heat exchanger is a complex of the following measures:
- replacing all seals after their service life has expired (4-6 years);
- complete cleaning of heat exchangers from deposits and scale;
- inspection of the plates for signs of corrosion, rejection of such plates.
Our company provides round-the-clock service for any heat exchangers (emergency service for cleaning and washing the plates in the heat exchanger), as well as an emergency repair service for heat exchangers of any complexity. We also carry out work to maintain the constant functionality of your equipment.
You can enter into a service contract or arrange individual visits. The important thing is that you can control the situation without allowing problems to arise.
We always have in stock the main components and spare parts for the types of heating equipment we service.
As you can see from the photo, timely maintenance is an IMPORTANT condition for stable operation. The seals and some plates have become unusable - they need to be washed.
Warm Company specialists clean the plates in an acid bath and wash the plates under pressure.
Types of cleaning solutions
Three types of cleaning products are produced for cleaning plate heat exchangers:
- powders;
- concentrated liquids;
- ready-made solutions.
The first two types are called reagents. They require preparation before use. The products are diluted with water in the proportion specified by the manufacturer.
Figure 3 — Plaque in the heat exchanger pipe
Composition of the cleaning agent
Modern reagents and ready-made solutions are characterized by a wide range of chemical active ingredients in their composition. Concentrates may include:
- organic acids;
- acid corrosion inhibitors (prevent the destruction of system elements);
- chemical reagents;
- defoamers;
- components that form a protective film on internal surfaces.
The detergent must loosen carbonate contamination, transform it into a liquid state for removal from the system. Many manufacturers offer substances that change the color of the liquid to control the process. This eliminates the need to use test strips to measure pH levels at various stages of cleaning.
Selection of detergents by type of contamination
| Type of pollution | Cleaning agent |
| Scale and metal deposits | Phosphoric, citric, nitric acids |
| Iron oxide | Inhibited mineral solution of high acidity |
| Organic compounds | Sodium alkali |
| Mineral contamination | Nitric acid |
| Fatty stains | Special solvents |
An alternative to chemicals is a mixture based on caustic soda and sodium carbonate. It is less harmful to human health, but is not able to eliminate all contaminants. It can be used to remove fats, oils, and biological substances.
Flushing a gas boiler
A gas boiler can be cleaned at home. The need to do this arises when the following symptoms occur:
- the characteristic hum of the circulation pump, which indicates an overload of the system;
- burner operating without interruption;
- long heating of the radiator;
- low water pressure (double-circuit boilers);
- increase in gas consumption.
The following preparations are applicable for home cleaning:
- Lemon acid. It effectively removes scale if the solution is heated to 60 degrees. Suitable for cleaning systems made of brass, copper, stainless steel.
- Sulfamic and adipic acids. Sufficient for regular cleaning with light soiling. Eliminate metal oxides. Suitable for equipment made from different metals.
- Hydrochloric acid. Removes heavy sediment. Used for heat exchangers made of copper and steel. However, it can be dangerous for products made of other metals.
- Orthophosphoric acid. Removes scale and dirt. An additional benefit is the formation of a protective film.
- Water-soluble gels. They are slightly aggressive towards equipment elements and remove dirt well.
When cleaning boilers and heat exchangers, it is important to take precautions - wear goggles, gloves, and respirators.
Figure 4 - Protection of the respiratory system, eyesight and hands when flushing the heat exchanger with chemicals
Why is scale dangerous?
Few people argue that the problem exists, but not everyone knows what its consequences are. The accumulation of deposits on the fins of the heat exchanger has a bad effect on the operation of the heating system:
- Increases fuel consumption . Metal is used in heating system components not only because of its rigidity, but also due to its thermal conductivity properties. Scale does not have such thermal conductivity, and the boiler has to spend more time and fuel on heating. Just 1mm of deposits on the heat exchanger and gas bills will increase by 10%.
- Overheating of the heat exchange element . Heating boilers have a water cooling system that comes from the return line. But when scale forms on the heat exchanger, the system becomes confused, using more force to heat. The problem is fraught not only with increased gas consumption, but also with overheating of the element, which can even damage it.
- Increased load on the heating system . When formations appear on the surface of the nodes, the channels narrow significantly, which impairs the process of water circulation. The workload of the circulation pump system increases, which is why it can also break down.
The harmful effects of scale Source vyborradiatora.ru