How is gasoline separated from coal?
It is worth noting that the processing of coal in order to obtain different types of motor fuel is not a myth at all. Moreover, there are two proven methods that were put into practice at the beginning of the last century.
In those days, Nazi Germany, striving to conquer all of Europe, provided its military equipment with fuel precisely in these ways, since it did not have its own oil deposits. At the same time, the country had deposits of brown coal, from which synthetic gasoline and diesel fuel were produced at two dozen factories.
For reference. Both methods were invented by different German scientists at the beginning of the 20th century, and accordingly received their names.
As it turns out, coal is not very different in chemical composition from oil. They have a common basis - flammable compounds of carbon with hydrogen, only the proportion of hydrogen in oil is much greater. If the amount of hydrogen in coal can be equalized with oil, then the production of liquid fuel will become a reality. Here are ways to solve the problem:
- hydrogenation, otherwise known as liquefaction (Bergius process).
- gasification followed by fuel synthesis (Fischer–Tropsch process).
To understand whether it will be possible to establish the separation of gasoline at home, you need to get a general understanding of these chemical and technological processes, which will be discussed below.
Help with poisoning
It is important to know that the sooner help is provided for poisoning, the greater the effect that can be achieved. At the first signs of ill health, you need to take 6-8 tablets of activated carbon, washing them down with enough water. Crushed tablets can be mixed in a glass of water and drunk
Considering that charcoal does not dissolve in water, the resulting suspension must be shaken thoroughly before use.
The crushed tablets can be mixed in a glass of water and drunk. Considering that charcoal does not dissolve in water, the resulting suspension must be shaken thoroughly before use.
At the first signs of ill health, you need to take 6-8 tablets of activated carbon, washing them down with enough water. The crushed tablets can be mixed in a glass of water and drunk. Considering that charcoal does not dissolve in water, the resulting suspension must be shaken thoroughly before use.
The drug is continued until recovery, drinking 3-4 tablets at a time.
In case of acute intoxication, first cleanse the stomach with charcoal diluted in water (10-20 g of charcoal per 0.1 liter of water), and then give the patient 6-8 tablets.
Alcohol poisoning is treated according to the same scheme; the instructions for the drug recommend taking 3-5 tablets an hour or two before alcohol to reduce the damage done to the body.
In case of severe vomiting, you must first take antiemetic drugs, and only then take activated charcoal.
Hydrogenation process
To successfully carry out the process and obtain up to 800 kg of liquid fuel from 1 ton of raw materials, brown or hard coal is taken. The main condition for effectively achieving results is the presence of 35% volatile substances in coals. Before processing, they are ground, crushed to a dusty fraction, and then dried. After this, the coal fraction is mixed with fuel oil or heavy oils to form raw materials in the form of a paste.
During the destructive hydrogenation process, the technology involves direct addition of the missing hydrogen to the coal.
To do this, the raw materials are placed in a special autoclave and heated. In this case, the pressure inside the vessel reaches 200 Bar, and the temperature – 500 °C. Moreover, there must be substances in the chemical reaction zone - catalysts and solvents. According to this method, the production of gasoline from coal takes place inside an autoclave in 2 stages:
- liquid phase;
- vapor phase.
Several complex chemical reactions take place in a vessel under high pressure and high temperature. In order not to burden the story with specific terms, let us explain in simple words: in the autoclave, coal is saturated with hydrogen and complex organic compounds decompose into simple ones. As a result, after cleaning operations, the output is synthetic diesel fuel or gasoline. This depends on the conditions of the process and the degree of transformation of the coal-oil mixture. But the exit of fuel from the installation is preceded by a number of operations:
- centrifugation;
- semi-coking;
- distillation.
As you can see, it is not possible to set up such a complex production with your own hands. The main difficulty is the equipment; it is unlikely that you will be able to make it yourself. Take, for example, an autoclave, where the pressure is higher than in oxygen cylinders. And in general, such production poses an explosion and fire hazard.
Coal
Coal is much more popular in the fuel energy industry. It is much older than brown coal - the age of rock deposits is about 350 million years. Coal is a much stronger, harder and heavier mineral, which usually lies at depths of 2 km.
This black rock with a matte sheen contains 75-95% carbon and only 5-6% moisture. Due to the high heat of combustion - about 5500-7500 kcal/kg - hard coal burns much better than brown coal.
According to the degree of coalification, hard coal is divided into many varieties. Among the grades of coal today there are long-flame (D), gas (G), fat (Zh), coke fat (KZh), coke (K), lean sintering (OS), lean (T) and anthracite (A).
All subtypes of coal differ in the degree of release of volatile substances, elemental composition, calorific value, volumetric weight and yield of volatile substances. For example, for coal grades G and D, the yield of volatile substances is 30-50%, grades T - 13%, grade A - 2-9%.
Lean coals contain a lot of carbon, but little volatile matter and bitumen. Gas and fat coals include coals with a high content of volatile substances. And coke coals have the highest calorific value - over 8 thousand kcal/kg.
The territory of Russia is replete with a number of coal basins, dispersed in a variety of regions. The main “coal” points are located in the Minusinsk, Kuznetsk, Lensk, Tunguska, Taimyr, Pechora, South Yakutsk and Bureya basins.
Thus, about 2.7 billion tons of coal lie in the Minusinsk basin. And in the Kuznetsk coal basin there are about 61.6 billion tons of proven coal reserves.
Also among the largest coal deposits is the Elginskoye deposit in Yakutia: its reserves are about 2.2 billion tons. Another deposit, Elegestskoye (Tuva), has reserves of about 20 billion tons.
Producing gasoline by gasification
This method, invented by German scientists F. Fischer and G. Tropsch, involves the production of diesel fuel and gasoline by preliminary gasification of coal raw materials. This occurs in a large container - a reactor at temperatures up to 350 ° C and a pressure of no more than 30 Bar. Although the conditions here are not as stringent as for hydrogenation, they are no easier to implement. For example, because superheated water vapor must be blown through a layer of coal under high pressure, which means you cannot do without a powerful steam boiler.
After gasification, the so-called synthesis gas is formed at the outlet of the reactor, consisting of hydrogen and ordinary carbon monoxide (CO). By the way, syngas can be directly used as a gaseous fuel without further processing.
The resulting gases enter the second reactor, where the final processing of coal into liquid fuel occurs. Substances called catalysts are also located there. In industry, different compounds can be used for this purpose, but any of them necessarily contains iron, nickel or cobalt. Without going into the intricacies of chemistry, we note that the output from the second reactor produces fuel, which must still undergo a cracking procedure. That is, the division into gasoline and diesel fuel from coal.
By-products of the reaction are various substances and paraffin. Among the volatile substances released, the largest share is carbon dioxide, which is considered a big problem in the production of fuel using this method. The catalyst also loses activity quite quickly, so it constantly needs to be renewed. These factors, and a number of less significant reasons, lead to the high cost of the product. With an oil price of $50 per barrel, the production of gasoline from coal using the Fischer-Tropsch method is considered unprofitable.
There is another method of coal gasification - thermal. It is similar to the phenomenon of pyrolysis, since it is carried out by heating the raw material in a container from the outside and in the absence of oxygen. Another thing is that the decomposition of solid fuel into gases occurs at a temperature of 1200 ° C, and this requires appropriate equipment. The positive side of the thermal method is that part of the pyrolysis gases is directed to heating the feedstock, and the other to the synthesis of gasoline. Due to this, energy costs are reduced, since coal can heat itself during decomposition.
For reference. On the Internet you can find descriptions of various installations with which you can obtain gasoline from natural gas at home. It is first converted into synthesis gas and then processed into liquid fuel. Even if we assume that these homemade devices are functional, gasifying coal is much more difficult.
Demonstration projects and commercial development
The 250-kilowatt methane synthesis plant was built by the Center for Solar Energy and Hydrogen Research (ZSW) in Baden-Württemberg and the Fraunhofer Society in Germany and began operating in 2010. It is being upgraded to 10 megawatts and is scheduled for completion in the fall. 2012
George Olah's carbon dioxide recycling plant, operated by Carbon Recycling International in Grindavik, Iceland, has been producing 2 million liters of methanol transport fuel per year from flue gases from the Svartsengi power station since 2008. Its capacity is 5 million liters per year. .
Audi has built a zero-carbon liquefied natural gas (LNG) plant in Werlte, Germany. The plant is designed to produce transportation fuel to offset the CNG used in their cars, and can hold 2,800 metric tons of CO2 per year at its original capacity.
Commercial development is underway in Columbia, South Carolina, Camarillo, California, and Darlington, England. A demonstration project in Berkeley, California, proposes the synthesis of fuels and edible oils from recovered flue gases.
conclusions
Despite the fact that the separation of motor fuel from hard and brown coal is quite real and has long been tested in production, it is hardly possible to organize it at home. Of course, there will always be a few craftsmen - enthusiasts who love to achieve their goals and will be able to synthesize gasoline with their own hands. But to do this, you need to study the technology in detail and tinker a lot with the equipment, not to mention the fire hazard.
For a wide range of homeowners and car enthusiasts, obtaining diesel fuel and gasoline from coal is not available. And if you approach the issue from an economic point of view, then it is unprofitable. At the moment, until new inventions and developments have appeared on this topic, it is easier and more reliable to use regular, “petroleum” gasoline.
What makes it possible to ensure high heat transfer from smokeless briquettes? And how did you measure it?
Sergey Stepanov:
To measure heat transfer, 10 kilograms of briquettes were burned in a household boiler, and the supply of useful heat (hot water) was determined using a heat meter.
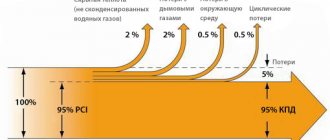
The high efficiency of the boiler is ensured by the fact that the boiler operates evenly most of the time. When burning coal, the combustion mode is different - first there is a peak heat release, then attenuation. Therefore, with coal, most of the heat simply flies away into the chimney.
By the way, when we talk about high heat transfer and fuel economy, it is important to understand that you need to load briquettes in the same volume as you usually load coal. The fact that you need 1.5-2 times less briquettes for heating means that you will have to load fuel 1.5-2 times less often
There is no need to reduce the single portion of loading!
Oil fractions
- The fraction collected from 40 to 200°C—the gasoline fraction—contains hydrocarbons from C6H12 to C11H24.
- The naphtha fraction, collected between 150 and 250 °C, contains hydrocarbons from C8H18 to C14H30.
- The kerosene fraction includes hydrocarbons from C12H26 to C18H38 with a boiling point from 180 to 300°C.
- The next fraction produces gas oil (above 275°C) - diesel fuel.
- The residue after oil distillation - fuel oil - contains hydrocarbons with a large number of carbon atoms (up to many tens) in the molecule. After distillation, tar remains. It is used in road construction.